 |
PDBsum entry 3smb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/isomerase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3smb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase/isomerase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Phenethylisothiocyanate covalently bound to macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: mif, glycosylation-inhibiting factor, gif, l-dopachrome isomerase, l-dopachrome tautomerase, phenylpyruvate tautomerase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: glif, mif, mmif. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.181
|
R-free:
|
0.197
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow,E.J.Lolis
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow
et al.
(2012).
Structural interactions dictate the kinetics of macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibition by different cancer-preventive isothiocyanates.
Biochemistry,
51,
7506-7514.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Jun-11
|
Release date:
|
03-Oct-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14174
(MIF_HUMAN) -
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
115 a.a.
114 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.2.1
- phenylpyruvate tautomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phenylpyruvate = enol-phenylpyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phenylpyruvate
|
=
|
enol-phenylpyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 53.33% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.12
- L-dopachrome isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dopachrome = 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-dopachrome
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 56.25% similarity
|
=
|
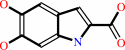 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
51:7506-7514
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural interactions dictate the kinetics of macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibition by different cancer-preventive isothiocyanates.
|
|
G.V.Crichlow,
C.Fan,
C.Keeler,
M.Hodsdon,
E.J.Lolis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Regulation of cellular processes by dietary nutrients is known to affect the
likelihood of cancer development. One class of cancer-preventive nutrients,
isothiocyanates (ITCs), derived from the consumption of cruciferous vegetables,
is known to have various effects on cellular biochemistry. One target of ITCs is
macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), a widely expressed protein with
known inflammatory, pro-tumorigenic, pro-angiogenic, and anti-apoptotic
properties. MIF is covalently inhibited by a variety of ITCs, which in part may
explain how they exert their cancer-preventive effects. We report the
crystallographic structures of human MIF bound to phenethylisothiocyanate and to
l-sulforaphane (dietary isothiocyanates derived from watercress and broccoli,
respectively) and correlate structural features of these two isothiocyanates
with their second-order rate constants for MIF inactivation. We also
characterize changes in the MIF structure using nuclear magnetic resonance
heteronuclear single-quantum coherence spectra of these complexes and observe
many changes at the subunit interface. While a number of chemical shifts do not
change, many of those that change do not have features similar in magnitude or
direction for the two isothiocyanates. The difference in the binding modes of
these two ITCs provides a means of using structure-activity relationships to
reveal insights into MIF biological interactions. The results of this study
provide a framework for the development of therapeutics that target MIF.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

