 |
PDBsum entry 3o2g

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3o2g
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human gamma-butyrobetaine,2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase 1 (bbox1)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase. Chain: a. Synonym: gamma-butyrobetaine,2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase, gamma- butyrobetaine hydroxylase, gamma-bbh. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: bbox1, bbh, bbox. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.78Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.149
|
R-free:
|
0.176
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Krojer,G.Kochan,M.A.Mcdonough,F.Von Delft,I.K.H.Leung,L.Henry, T.D.W.Claridge,E.Pilka,E.Ugochukwu,J.Muniz,P.Filippakopoulos, C.Bountra,C.H.Arrowsmith,J.Weigelt,A.Edwards,K.L.Kavanagh, C.J.Schofield,U.Oppermann,Structural Genomics Consortium (Sgc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
I.K.Leung
et al.
(2010).
Structural and mechanistic studies on γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase.
Chem Biol,
17,
1316-1324.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Jul-10
|
Release date:
|
15-Sep-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O75936
(BODG_HUMAN) -
Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
387 a.a.
386 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.1
- gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-(trimethylamino)butanoate + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = carnitine + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-(trimethylamino)butanoate
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
carnitine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.91% similarity
|
+
|
succinate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.00% similarity
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+); L-ascorbate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(2+)
|
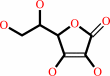 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chem Biol
17:1316-1324
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and mechanistic studies on γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase.
|
|
I.K.Leung,
T.J.Krojer,
G.T.Kochan,
L.Henry,
F.von Delft,
T.D.Claridge,
U.Oppermann,
M.A.McDonough,
C.J.Schofield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The final step in carnitine biosynthesis is catalyzed by γ-butyrobetaine (γBB)
hydroxylase (BBOX), an iron/2-oxoglutarate (2OG) dependent oxygenase. BBOX is
inhibited by trimethylhydrazine-propionate (THP), a clinically used compound. We
report structural and mechanistic studies on BBOX and its reaction with THP.
Crystallographic and sequence analyses reveal that BBOX and trimethyllysine
hydroxylase form a subfamily of 2OG oxygenases that dimerize using an N-terminal
domain. The crystal structure reveals the active site is enclosed and how THP
competes with γBB. THP is a substrate giving formaldehyde (supporting
structural links with histone demethylases), dimethylamine, malonic acid
semi-aldehyde, and an unexpected product with an additional carbon-carbon bond
resulting from N-demethylation coupled to oxidative rearrangement, likely via an
unusual radical mechanism. The results provide a basis for development of
improved BBOX inhibitors and may inspire the discovery of additional
rearrangement reactions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

