 |
PDBsum entry 3k3h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the pde9a catalytic domain in complex with (s)- bay73-6691
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
High affinity cgmp-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9a. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic domain: unp residues 241-566. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pde9a, pde9a2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.223
|
R-free:
|
0.245
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Wang,X.Luo,M.Ye,J.Hou,H.Robinson,H.Ke
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Wang
et al.
(2010).
Insight into binding of phosphodiesterase-9A selective inhibitors by crystal structures and mutagenesis.
J Med Chem,
53,
1726-1731.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-Oct-09
|
Release date:
|
16-Feb-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O76083
(PDE9A_HUMAN) -
High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
593 a.a.
321 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.35
- 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3',5'-cyclic GMP + H2O = GMP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 3',5'-cyclic GMP
3',5'-cyclic GMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
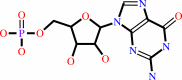 GMP
GMP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Med Chem
53:1726-1731
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insight into binding of phosphodiesterase-9A selective inhibitors by crystal structures and mutagenesis.
|
|
H.Wang,
X.Luo,
M.Ye,
J.Hou,
H.Robinson,
H.Ke.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
PDE9 inhibitors have been studied as therapeutics for treatment of
cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. To
illustrate the inhibitor selectivity, the crystal structures of the PDE9A
catalytic domain in complex with the enantiomers of PDE9 inhibitor
1-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-(3,3,3-trifluoro-2-methylpropyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4(5H)-one
((R)-BAY73-6691 or (S)-BAY73-6691, 1r or 1s) were determined and mutagenesis was
performed. The structures showed that the fluoromethyl groups of 1r and 1s had
different orientations while the other parts of the inhibitors commonly
interacted with PDE9A. These differences may explain the slightly different
affinity of 1r (IC(50) = 22 nM) and 1s (IC(50) = 88 nM). The mutagenesis
experiments revealed that contribution of the binding residues to the inhibitor
sensitivity varies dramatically, from few-fold to 3 orders of magnitude. On the
basis of the crystal structures, a hypothesized compound that simulates the
recently published PDE9 inhibitors was modeled to provide insight into the
inhibitor selectivity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Hou,
J.Xu,
M.Liu,
R.Zhao,
H.B.Luo,
and
H.Ke
(2011).
Structural asymmetry of phosphodiesterase-9, potential protonation of a glutamic acid, and role of the invariant glutamine.
|
| |
PLoS One,
6,
e18092.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

