 |
PDBsum entry 3itx

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase, metal-binding protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3itx
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase, metal-binding protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Mn2+ bound form of pseudomonas stutzeri l-rhamnose isomerase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
L-rhamnose isomerase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pseudomonas stutzeri. Pseudomonas perfectomarina. Organism_taxid: 316. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.165
|
R-free:
|
0.197
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Yoshida,M.Yamaji,T.Ishii,K.Izumori,S.Kamitori
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Yoshida
et al.
(2010).
Catalytic reaction mechanism of Pseudomonas stutzeri L-rhamnose isomerase deduced from X-ray structures.
Febs J,
277,
1045-1057.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Aug-09
|
Release date:
|
02-Feb-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q75WH8
(Q75WH8_STUST) -
L-rhamnose isomerase from Stutzerimonas stutzeri
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
430 a.a.
420 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.14
- L-rhamnose isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-rhamnopyranose = L-rhamnulose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-rhamnopyranose
|
=
|
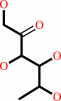 L-rhamnulose
L-rhamnulose
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Divalent cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Febs J
277:1045-1057
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Catalytic reaction mechanism of Pseudomonas stutzeri L-rhamnose isomerase deduced from X-ray structures.
|
|
H.Yoshida,
M.Yamaji,
T.Ishii,
K.Izumori,
S.Kamitori.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
L-Rhamnose isomerase (L-RhI) catalyzes the reversible isomerization of
L-rhamnose to L-rhamnulose. Pseudomonas stutzeril-RhI, with a broad substrate
specificity, can catalyze not only the isomerization of L-rhamnose, but also
that between D-allose and D-psicose. For the aldose-ketose isomerization by
L-RhI, a metal-mediated hydride-shift mechanism has been proposed, but the
catalytic mechanism is still not entirely understood. To elucidate the entire
reaction mechanism, the X-ray structures of P. stutzeril-RhI in an Mn(2+)-bound
form, and of two inactive mutant forms of P. stutzeril-RhI (S329K and D327N) in
a complex with substrate/product, were determined. The structure of the
Mn(2+)-bound enzyme indicated that the catalytic site interconverts between two
forms with the displacement of the metal ion to recognize both pyranose and
furanose ring substrates. Solving the structures of S329K-substrates allowed us
to examine the metal-mediated hydride-shift mechanism of L-RhI in detail. The
structural analysis of D327N-substrates and additional modeling revealed Asp327
to be responsible for the ring opening of furanose, and a water molecule
coordinating with the metal ion to be involved in the ring opening of pyranose.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Yoshida,
K.Takeda,
K.Izumori,
and
S.Kamitori
(2010).
Elucidation of the role of Ser329 and the C-terminal region in the catalytic activity of pseudomonas stutzeri L-rhamnose isomerase.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
919-927.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

