 |
PDBsum entry 3fty

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.3.2.6
- leukotriene-A4 hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
leukotriene A4 + H2O = leukotriene B4
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
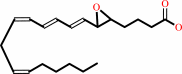 leukotriene A4
leukotriene A4
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 46.15% similarity
|
=
|
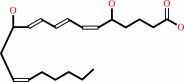 leukotriene B4
leukotriene B4
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.4.11.4
- tripeptide aminopeptidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Release of a N-terminal residue from a tripeptide.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Med Chem
52:4694-4715
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Discovery of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors using metabolomics biased fragment crystallography.
|
|
D.R.Davies,
B.Mamat,
O.T.Magnusson,
J.Christensen,
M.H.Haraldsson,
R.Mishra,
B.Pease,
E.Hansen,
J.Singh,
D.Zembower,
H.Kim,
A.S.Kiselyov,
A.B.Burgin,
M.E.Gurney,
L.J.Stewart.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We describe a novel fragment library termed fragments of life (FOL) for
structure-based drug discovery. The FOL library includes natural small molecules
of life, derivatives thereof, and biaryl protein architecture mimetics. The
choice of fragments facilitates the interrogation of protein active sites,
allosteric binding sites, and protein-protein interaction surfaces for fragment
binding. We screened the FOL library against leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H) by
X-ray crystallography. A diverse set of fragments including derivatives of
resveratrol, nicotinamide, and indole were identified as efficient ligands for
LTA4H. These fragments were elaborated in a small number of synthetic cycles
into potent inhibitors of LTA4H representing multiple novel chemotypes for
modulating leukotriene biosynthesis. Analysis of the fragment-bound structures
also showed that the fragments comprehensively recapitulated key chemical
features and binding modes of several reported LTA4H inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.W.Lee,
A.M.Bode,
and
Z.Dong
(2011).
Molecular targets of phytochemicals for cancer prevention.
|
| |
Nat Rev Cancer,
11,
211-218.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Thangapandian,
S.John,
S.Sakkiah,
and
K.W.Lee
(2011).
Pharmacophore-based virtual screening and Bayesian model for the identification of potential human leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors.
|
| |
Eur J Med Chem,
46,
1593-1603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Murray,
and
T.L.Blundell
(2010).
Structural biology in fragment-based drug design.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
20,
497-507.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.I.Brelidze,
A.E.Carlson,
D.R.Davies,
L.J.Stewart,
and
W.N.Zagotta
(2010).
Identifying regulators for EAG1 channels with a novel electrophysiology and tryptophan fluorescence based screen.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
0.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.C.Van Voorhis,
W.G.Hol,
P.J.Myler,
and
L.J.Stewart
(2009).
The role of medical structural genomics in discovering new drugs for infectious diseases.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
5,
e1000530.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

