 |
PDBsum entry 3dyn

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Human phosphodiestrase 9 in complex with cgmp (zn inhibited)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
High affinity cgmp-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9a. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic domain, unp residues 242-566. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pde9a. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.183
|
R-free:
|
0.203
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Liu,M.N.Mansour,K.Dillman,J.Perez,D.Danley,F.Menniti
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Liu
et al.
(2008).
Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism of human phosphodiesterase 9.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
13309-13314.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Jul-08
|
Release date:
|
16-Sep-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O76083
(PDE9A_HUMAN) -
High affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
593 a.a.
328 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.35
- 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3',5'-cyclic GMP + H2O = GMP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3',5'-cyclic GMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
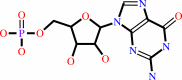 GMP
GMP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
105:13309-13314
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism of human phosphodiesterase 9.
|
|
S.Liu,
M.N.Mansour,
K.S.Dillman,
J.R.Perez,
D.E.Danley,
P.A.Aeed,
S.P.Simons,
P.K.Lemotte,
F.S.Menniti.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are metal ion-dependent enzymes that regulate
cellular signaling by metabolic inactivation of the ubiquitous second messengers
cAMP and cGMP. In this role, the PDEs are involved in many biological and
metabolic processes and are proven targets of successful drugs for the
treatments of a wide range of diseases. However, because of the rapidity of the
hydrolysis reaction, an experimental knowledge of the enzymatic mechanisms of
the PDEs at the atomic level is still lacking. Here, we report the structures of
reaction intermediates accumulated at the reaction steady state in PDE9/crystal
and preserved by freeze-trapping. These structures reveal the catalytic process
of a PDE and explain the substrate specificity of PDE9 in an actual reaction and
the cation requirements of PDEs in general.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Stereo diagram of the putative ES complex model illustrates
the recognition of cGMP (magenta carbons) by active PDE9 (green
carbons). Hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of the proposed reaction pathway for
PDE9. E, apo enzyme. ES, enzyme/substrate. EP, enzyme/product
complex. E+P, the regenerated enzyme/rebound product complexes.
Dashed lines represent hydrogen/coordination bonds.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Hou,
J.Xu,
M.Liu,
R.Zhao,
H.B.Luo,
and
H.Ke
(2011).
Structural asymmetry of phosphodiesterase-9, potential protonation of a glutamic acid, and role of the invariant glutamine.
|
| |
PLoS One,
6,
e18092.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Wang,
X.Luo,
M.Ye,
J.Hou,
H.Robinson,
and
H.Ke
(2010).
Insight into binding of phosphodiesterase-9A selective inhibitors by crystal structures and mutagenesis.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
53,
1726-1731.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.X.He,
L.Huang,
Y.Xue,
X.Fei,
Y.B.Teng,
S.B.Rubin-Pitel,
H.Zhao,
and
C.Z.Zhou
(2010).
Crystal structure and computational analyses provide insights into the catalytic mechanism of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol hydrolase PhlG from Pseudomonas fluorescens.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
4603-4611.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Pandit,
M.D.Forman,
K.F.Fennell,
K.S.Dillman,
and
F.S.Menniti
(2009).
Mechanism for the allosteric regulation of phosphodiesterase 2A deduced from the X-ray structure of a near full-length construct.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
18225-18230.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

