 |
PDBsum entry 3box

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of l-rhamnonate dehydratase from salmonella typhimurium complexed with mg
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
L-rhamnonate dehydratase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: putative galactonate dehydratase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Salmonella typhimurium lt2. Organism_taxid: 99287. Strain: lt2, sgsc1412. Atcc: 700720. Gene: yfaw, stm2291. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.201
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.A.Fedorov,E.V.Fedorov,J.M.Sauder,S.K.Burley,J.A.Gerlt,S.C.Almo,New York Sgx Research Center For Structural Genomics (Nysgxrc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.F.Rakus
et al.
(2008).
Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: L-rhamnonate dehydratase.
Biochemistry,
47,
9944-9954.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-Dec-07
|
Release date:
|
01-Jan-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q8ZNF9
(RHMD_SALTY) -
L-rhamnonate dehydratase from Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
405 a.a.
402 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.90
- L-rhamnonate dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-rhamnonate = 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
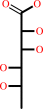 L-rhamnonate
L-rhamnonate
|
=
|
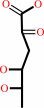 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:9944-9954
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Evolution of enzymatic activities in the enolase superfamily: L-rhamnonate dehydratase.
|
|
J.F.Rakus,
A.A.Fedorov,
E.V.Fedorov,
M.E.Glasner,
B.K.Hubbard,
J.D.Delli,
P.C.Babbitt,
S.C.Almo,
J.A.Gerlt.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The l-rhamnonate dehydratase (RhamD) function was assigned to a previously
uncharacterized family in the mechanistically diverse enolase superfamily that
is encoded by the genome of Escherichia coli K-12. We screened a library of acid
sugars to discover that the enzyme displays a promiscuous substrate specificity:
l-rhamnonate (6-deoxy- l-mannonate) has the "best" kinetic constants, with
l-mannonate, l-lyxonate, and d-gulonate dehydrated less efficiently. Crystal
structures of the RhamDs from both E. coli K-12 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2
(95% sequence identity) were obtained in the presence of Mg (2+); the structure
of the RhamD from S. typhimurium was also obtained in the presence of 3-deoxy-
l-rhamnonate (obtained by reduction of the product with NaBH 4). Like other
members of the enolase superfamily, RhamD contains an N-terminal alpha + beta
capping domain and a C-terminal (beta/alpha) 7beta-barrel (modified TIM-barrel)
catalytic domain with the active site located at the interface between the two
domains. In contrast to other members, the specificity-determining "20s loop" in
the capping domain is extended in length and the "50s loop" is truncated. The
ligands for the Mg (2+) are Asp 226, Glu 252 and Glu 280 located at the ends of
the third, fourth and fifth beta-strands, respectively. The active site of RhamD
contains a His 329-Asp 302 dyad at the ends of the seventh and sixth
beta-strands, respectively, with His 329 positioned to function as the general
base responsible for abstraction of the C2 proton of l-rhamnonate to form a Mg
(2+)-stabilized enediolate intermediate. However, the active site does not
contain other acid/base catalysts that have been implicated in the reactions
catalyzed by other members of the MR subgroup of the enolase superfamily. Based
on the structure of the liganded complex, His 329 also is expected to function
as the general acid that both facilitates departure of the 3-OH group in a
syn-dehydration reaction and delivers a proton to carbon-3 to replace the 3-OH
group with retention of configuration.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Erdin,
R.M.Ward,
E.Venner,
and
O.Lichtarge
(2010).
Evolutionary trace annotation of protein function in the structural proteome.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
396,
1451-1473.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Rakus,
C.Kalyanaraman,
A.A.Fedorov,
E.V.Fedorov,
F.P.Mills-Groninger,
R.Toro,
J.Bonanno,
K.Bain,
J.M.Sauder,
S.K.Burley,
S.C.Almo,
M.P.Jacobson,
and
J.A.Gerlt
(2009).
Computation-facilitated assignment of the function in the enolase superfamily: a regiochemically distinct galactarate dehydratase from Oceanobacillus iheyensis .
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
11546-11558.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zhang,
F.Gao,
H.Peng,
H.Cheng,
Y.Liu,
J.Tang,
J.Thompson,
G.Wei,
J.Zhang,
Y.Du,
J.Yan,
and
G.F.Gao
(2009).
Crystal structures of Streptococcus suis mannonate dehydratase (ManD) and its complex with substrate: genetic and biochemical evidence for a catalytic mechanism.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
5832-5837.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Copley
(2009).
Prediction of function in protein superfamilies.
|
| |
F1000 Biol Rep,
1,
0.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Watanabe,
and
K.Makino
(2009).
Novel modified version of nonphosphorylated sugar metabolism--an alternative L-rhamnose pathway of Sphingomonas sp.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
1554-1567.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

