
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Immune system
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of tlr2-pe-dtpa complex
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Toll-like receptor 2, variable lymphocyte receptor b. Chain: a. Fragment: extracellular domain, unp residues 1-506(mouse), unp residues 133-200(inshore hagfish). Synonym: tlr2, vlrb.61. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus, eptatretus burgeri. Mouse, inshore hagfish. Organism_taxid: 10090, 7764. Gene: tlr2. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.215
|
R-free:
|
0.290
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Y.Kang,M.S.Jin,J.-O.Lee
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Y.Kang
et al.
(2009).
Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer.
Immunity,
31,
873-884.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Sep-09
|
Release date:
|
24-Nov-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.2.6
- ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + H2O = ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
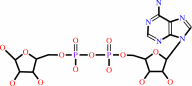 ADP-D-ribose
ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
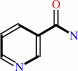 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 43.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Immunity
31:873-884
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer.
|
|
J.Y.Kang,
X.Nan,
M.S.Jin,
S.J.Youn,
Y.H.Ryu,
S.Mah,
S.H.Han,
H.Lee,
S.G.Paik,
J.O.Lee.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) initiates potent immune responses by recognizing
diacylated and triacylated lipopeptides. Its ligand specificity is controlled by
whether it heterodimerizes with TLR1 or TLR6. We have determined the crystal
structures of TLR2-TLR6-diacylated lipopeptide, TLR2-lipoteichoic acid, and
TLR2-PE-DTPA complexes. PE-DTPA,
1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic
acid, is a synthetic phospholipid derivative. Two major factors contribute to
the ligand specificity of TLR2-TLR1 or TLR2-TLR6 heterodimers. First, the lipid
channel of TLR6 is blocked by two phenylalanines. Simultaneous mutation of these
phenylalanines made TLR2-TLR6 fully responsive not only to diacylated but also
to triacylated lipopeptides. Second, the hydrophobic dimerization interface of
TLR2-TLR6 is increased by 80%, which compensates for the lack of amide lipid
interaction between the lipopeptide and TLR2-TLR6. The structures of the
TLR2-lipoteichoic acid and the TLR2-PE-DTPA complexes demonstrate that a precise
interaction pattern of the head group is essential for a robust immune response
by TLR2 heterodimers.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Lal,
N.Yin,
J.Xu,
M.Lin,
S.Schroppel,
Y.Ding,
I.Marie,
D.E.Levy,
and
J.S.Bromberg
(2011).
Distinct inflammatory signals have physiologically divergent effects on epigenetic regulation of foxp3 expression and treg function.
|
| |
Am J Transplant,
11,
203-214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Botos,
D.M.Segal,
and
D.R.Davies
(2011).
The structural biology of Toll-like receptors.
|
| |
Structure,
19,
447-459.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Khoo,
S.Forster,
and
A.Mansell
(2011).
Toll-like receptors as interferon-regulated genes and their role in disease.
|
| |
J Interferon Cytokine Res,
31,
13-25.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Jang,
J.E.Baik,
S.H.Han,
D.K.Chung,
and
B.G.Kim
(2011).
Multi-spectrometric analyses of lipoteichoic acids isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum.
|
| |
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
407,
823-830.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.R.Schmidt,
C.M.Pedersen,
Y.Qiao,
and
U.Zähringer
(2011).
Chemical synthesis of bacterial lipoteichoic acids: an insight on its biological significance.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
9,
2040-2052.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.I.Yoon,
M.Hong,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2011).
An unusual dimeric structure and assembly for TLR4 regulator RP105-MD-1.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
18,
1028-1035.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Y.Sheng,
and
L.Huang
(2011).
Cancer immunotherapy and nanomedicine.
|
| |
Pharm Res,
28,
200-214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.J.Claes,
S.Lebeer,
C.Shen,
T.L.Verhoeven,
E.Dilissen,
G.De Hertogh,
D.M.Bullens,
J.L.Ceuppens,
G.Van Assche,
S.Vermeire,
P.Rutgeerts,
J.Vanderleyden,
and
S.C.De Keersmaecker
(2010).
Impact of lipoteichoic acid modification on the performance of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in experimental colitis.
|
| |
Clin Exp Immunol,
162,
306-314.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Drage,
H.C.Tsai,
N.D.Pecora,
T.Y.Cheng,
A.R.Arida,
S.Shukla,
R.E.Rojas,
C.Seshadri,
D.B.Moody,
W.H.Boom,
J.C.Sacchettini,
and
C.V.Harding
(2010).
Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein LprG (Rv1411c) binds triacylated glycolipid agonists of Toll-like receptor 2.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
17,
1088-1095.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yamamoto,
and
K.Takeda
(2010).
Current views of toll-like receptor signaling pathways.
|
| |
Gastroenterol Res Pract,
2010,
240365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Renaudet,
G.Dasgupta,
I.Bettahi,
A.Shi,
A.B.Nesburn,
P.Dumy,
and
L.BenMohamed
(2010).
Linear and branched glyco-lipopeptide vaccines follow distinct cross-presentation pathways and generate different magnitudes of antitumor immunity.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e11216.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Govindaraj,
B.Manavalan,
G.Lee,
and
S.Choi
(2010).
Molecular modeling-based evaluation of hTLR10 and identification of potential ligands in Toll-like receptor signaling.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e12713.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bas,
R.W.James,
and
C.Gabay
(2010).
Serum lipoproteins attenuate macrophage activation and Toll-Like Receptor stimulation by bacterial lipoproteins.
|
| |
BMC Immunol,
11,
46.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kawai,
and
S.Akira
(2010).
The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors.
|
| |
Nat Immunol,
11,
373-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Wang,
J.Jiang,
Q.Zhu,
A.Z.AlAnezi,
R.B.Clark,
X.Jiang,
D.W.Rowe,
and
F.C.Nichols
(2010).
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipids inhibit osteoblastic differentiation and function.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
78,
3726-3735.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Schenk,
J.T.Belisle,
and
R.L.Modlin
(2009).
TLR2 looks at lipoproteins.
|
| |
Immunity,
31,
847-849.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

