 |
PDBsum entry 2qb2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural studies reveal the inactivation of e. Coli l-aspartate aminotransferase by (s)-4,5-dihydro-2thiophenecarboylic acid (sadta) via two mechanisms (at ph 7.0).
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate aminotransferase. Chain: a. Synonym: transaminase a, aspat. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: aspc. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.147
|
R-free:
|
0.184
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.Liu,E.Pozharski,B.Lepore,M.Fu,R.B.Silverman,G.A.Petsko,D.Ringe
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.Liu
et al.
(2007).
Inactivation of Escherichia coli L-aspartate aminotransferase by (S)-4-amino-4,5-dihydro-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid reveals "a tale of two mechanisms".
Biochemistry,
46,
10517-10527.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Jun-07
|
Release date:
|
04-Dec-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00509
(AAT_ECOLI) -
Aspartate aminotransferase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
396 a.a.
384 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.1
- aspartate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate + 2-oxoglutarate = oxaloacetate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
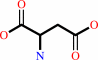 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
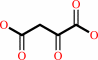 oxaloacetate
oxaloacetate
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PSZ)
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
46:10517-10527
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Inactivation of Escherichia coli L-aspartate aminotransferase by (S)-4-amino-4,5-dihydro-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid reveals "a tale of two mechanisms".
|
|
D.Liu,
E.Pozharski,
B.W.Lepore,
M.Fu,
R.B.Silverman,
G.A.Petsko,
D.Ringe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
As a mechanism-based inactivator of PLP-enzymes,
(S)-4-amino-4,5-dihydro-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid (SADTA) was cocrystallized
with Escherichia coli aspartate aminotransferase (l-AspAT) at a series of pH
values ranging from 6 to 8. Five structural models with high resolution
(1.4-1.85 A) were obtained for l-AspAT-SADTA complexes at pH 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5,
and 8.0. Electron densities of the models showed that two different adducts had
formed in the active sites. One adduct was formed from SADTA covalently linked
to pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) while the other adduct was formed with the
inhibitor covalently linked to Lysine246,1 the active site lysine. Moreover,
there is a strong indication based on the electron densities that the occurrence
of the two adducts is pH dependent. We conclude that SADTA inactivates l-AspAT
via two different mechanisms based on the binding direction of the inactivator.
Additionally, the structural models also show pH dependence of the protein
structure itself, which provided detailed mechanistic implications for l-AspAT.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

