 |
PDBsum entry 2oyc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human pyridoxal phosphate phosphatase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pyridoxal phosphate phosphatase. Chain: a. Synonym: plp phosphatase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pdxp, plp, plpp. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.72Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.193
|
R-free:
|
0.223
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
U.A.Ramagopal,J.Freeman,M.Izuka,R.Toro,J.M.Sauder,S.K.Burley, S.C.Almo,New York Sgx Research Center For Structural Genomics (Nysgxrc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.C.Almo
et al.
(2007).
Structural genomics of protein phosphatases.
J Struct Funct Genomics,
8,
121-140.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Feb-07
|
Release date:
|
13-Mar-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q96GD0
(PLPP_HUMAN) -
Chronophin from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
296 a.a.
292 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.16
- protein-serine/threonine phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + H2O = L-seryl-[protein] + phosphate
|
|
2.
|
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + H2O = L-threonyl-[protein] + phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.74
- pyridoxal phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H2O = pyridoxal + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
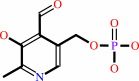 pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
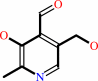 pyridoxal
pyridoxal
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Struct Funct Genomics
8:121-140
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural genomics of protein phosphatases.
|
|
S.C.Almo,
J.B.Bonanno,
J.M.Sauder,
S.Emtage,
T.P.Dilorenzo,
V.Malashkevich,
S.R.Wasserman,
S.Swaminathan,
S.Eswaramoorthy,
R.Agarwal,
D.Kumaran,
M.Madegowda,
S.Ragumani,
Y.Patskovsky,
J.Alvarado,
U.A.Ramagopal,
J.Faber-Barata,
M.R.Chance,
A.Sali,
A.Fiser,
Z.Y.Zhang,
D.S.Lawrence,
S.K.Burley.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The New York SGX Research Center for Structural Genomics (NYSGXRC) of the NIGMS
Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) has applied its high-throughput X-ray
crystallographic structure determination platform to systematic studies of all
human protein phosphatases and protein phosphatases from biomedically-relevant
pathogens. To date, the NYSGXRC has determined structures of 21 distinct protein
phosphatases: 14 from human, 2 from mouse, 2 from the pathogen Toxoplasma
gondii, 1 from Trypanosoma brucei, the parasite responsible for African sleeping
sickness, and 2 from the principal mosquito vector of malaria in Africa,
Anopheles gambiae. These structures provide insights into both normal and
pathophysiologic processes, including transcriptional regulation, regulation of
major signaling pathways, neural development, and type 1 diabetes. In
conjunction with the contributions of other international structural genomics
consortia, these efforts promise to provide an unprecedented database and
materials repository for structure-guided experimental and computational
discovery of inhibitors for all classes of protein phosphatases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Block,
and
Y.Gorin
(2012).
Aiding and abetting roles of NOX oxidases in cellular transformation.
|
| |
Nat Rev Cancer,
12,
627-637.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.T.Lountos,
J.E.Tropea,
and
D.S.Waugh
(2011).
Structure of human dual-specificity phosphatase 27 at 2.38 Å resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
67,
471-479.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.King-Scott,
P.V.Konarev,
S.Panjikar,
R.Jordanova,
D.I.Svergun,
and
P.A.Tucker
(2011).
Structural characterization of the multidomain regulatory protein Rv1364c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Structure,
19,
56-69.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.B.Karmacharya,
and
J.W.Soh
(2011).
Bioinformatic identification of novel protein phosphatases in the dog genome.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biochem,
351,
149-156.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Szöör
(2010).
Trypanosomatid protein phosphatases.
|
| |
Mol Biochem Parasitol,
173,
53-63.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Edwards
(2009).
Large-scale structural biology of the human proteome.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
78,
541-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Barr,
E.Ugochukwu,
W.H.Lee,
O.N.King,
P.Filippakopoulos,
I.Alfano,
P.Savitsky,
N.A.Burgess-Brown,
S.Müller,
and
S.Knapp
(2009).
Large-scale structural analysis of the classical human protein tyrosine phosphatome.
|
| |
Cell,
136,
352-363.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Molina,
A.Vogt,
A.Bakan,
W.Dai,
P.Queiroz de Oliveira,
W.Znosko,
T.E.Smithgall,
I.Bahar,
J.S.Lazo,
B.W.Day,
and
M.Tsang
(2009).
Zebrafish chemical screening reveals an inhibitor of Dusp6 that expands cardiac cell lineages.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
5,
680-687.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.T.Lountos,
J.E.Tropea,
S.Cherry,
and
D.S.Waugh
(2009).
Overproduction, purification and structure determination of human dual-specificity phosphatase 14.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
1013-1020.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Chattopadhyay,
E.Lazar-Molnar,
Q.Yan,
R.Rubinstein,
C.Zhan,
V.Vigdorovich,
U.A.Ramagopal,
J.Bonanno,
S.G.Nathenson,
and
S.C.Almo
(2009).
Sequence, structure, function, immunity: structural genomics of costimulation.
|
| |
Immunol Rev,
229,
356-386.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Melcher,
L.M.Ng,
X.E.Zhou,
F.F.Soon,
Y.Xu,
K.M.Suino-Powell,
S.Y.Park,
J.J.Weiner,
H.Fujii,
V.Chinnusamy,
A.Kovach,
J.Li,
Y.Wang,
J.Li,
F.C.Peterson,
D.R.Jensen,
E.L.Yong,
B.F.Volkman,
S.R.Cutler,
J.K.Zhu,
and
H.E.Xu
(2009).
A gate-latch-lock mechanism for hormone signalling by abscisic acid receptors.
|
| |
Nature,
462,
602-608.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Gentry,
J.E.Dixon,
and
C.A.Worby
(2009).
Lafora disease: insights into neurodegeneration from plant metabolism.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
34,
628-639.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Pieper,
R.Chiang,
J.J.Seffernick,
S.D.Brown,
M.E.Glasner,
L.Kelly,
N.Eswar,
J.M.Sauder,
J.B.Bonanno,
S.Swaminathan,
S.K.Burley,
X.Zheng,
M.R.Chance,
S.C.Almo,
J.A.Gerlt,
F.M.Raushel,
M.P.Jacobson,
P.C.Babbitt,
and
A.Sali
(2009).
Target selection and annotation for the structural genomics of the amidohydrolase and enolase superfamilies.
|
| |
J Struct Funct Genomics,
10,
107-125.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Moes,
A.Himmelbach,
A.Korte,
G.Haberer,
and
E.Grill
(2008).
Nuclear localization of the mutant protein phosphatase abi1 is required for insensitivity towards ABA responses in Arabidopsis.
|
| |
Plant J,
54,
806-819.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Burley,
A.Joachimiak,
G.T.Montelione,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2008).
Contributions to the NIH-NIGMS Protein Structure Initiative from the PSI Production Centers.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
5.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

