 |
PDBsum entry 2o4h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.15
- aspartoacylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an N-acyl-L-aspartate + H2O = a carboxylate + L-aspartate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
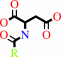 N-acyl-L-aspartate
N-acyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
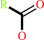 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
L-aspartate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 69.23% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:3484-3492
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Examination of the mechanism of human brain aspartoacylase through the binding of an intermediate analogue.
|
|
J.Le Coq,
A.Pavlovsky,
R.Malik,
R.Sanishvili,
C.Xu,
R.E.Viola.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Canavan disease is a fatal neurological disorder caused by the malfunctioning of
a single metabolic enzyme, aspartoacylase, that catalyzes the deacetylation of
N-acetyl-L-aspartate to produce L-aspartate and acetate. The structure of human
brain aspartoacylase has been determined in complex with a stable tetrahedral
intermediate analogue, N-phosphonomethyl-L-aspartate. This potent inhibitor
forms multiple interactions between each of its heteroatoms and the substrate
binding groups arrayed within the active site. The binding of the catalytic
intermediate analogue induces the conformational ordering of several substrate
binding groups, thereby setting up the active site for catalysis. The highly
ordered binding of this inhibitor has allowed assignments to be made for
substrate binding groups and provides strong support for a carboxypeptidase-type
mechanism for the hydrolysis of the amide bond of the substrate, N-acetyl-
l-aspartate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Zano,
R.Malik,
S.Szucs,
R.Matalon,
and
R.E.Viola
(2011).
Modification of aspartoacylase for potential use in enzyme replacement therapy for the treatment of Canavan disease.
|
| |
Mol Genet Metab,
102,
176-180.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Hsieh,
K.Tsirulnikov,
M.R.Sawaya,
N.Magilnick,
N.Abuladze,
I.Kurtz,
J.Abramson,
and
A.Pushkin
(2010).
Structures of aminoacylase 3 in complex with acetylated substrates.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
17962-17967.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Tsirulnikov,
N.Abuladze,
D.Newman,
S.Ryazantsev,
T.Wolak,
N.Magilnick,
M.C.Koag,
I.Kurtz,
and
A.Pushkin
(2009).
Mouse aminoacylase 3: a metalloenzyme activated by cobalt and nickel.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1794,
1049-1057.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Baslow,
and
D.N.Guilfoyle
(2009).
Are astrocytes the missing link between lack of brain aspartoacylase activity and the spongiform leukodystrophy in canavan disease?
|
| |
Neurochem Res,
34,
1523-1534.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

