 |
PDBsum entry 2h4l

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.2
- phosphoglucomutase (alpha-D-glucose-1,6-bisphosphate-dependent).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-glucose, UDP-galactose and UDP-glucuronate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 87.50% similarity
|
=
|
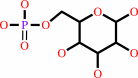 alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.8
- phosphomannomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate = D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 87.50% similarity
|
=
|
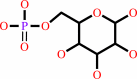 D-mannose 6-phosphate
D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallograph Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
62:722-726
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Complexes of the enzyme phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase with a slow substrate and an inhibitor.
|
|
C.Regni,
G.S.Shackelford,
L.J.Beamer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Two complexes of the enzyme phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase (PMM/PGM) from
Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a slow substrate and with an inhibitor have been
characterized by X-ray crystallography. Both ligands induce an interdomain
rearrangement in the enzyme that creates a highly buried active site.
Comparisons with enzyme-substrate complexes show that the inhibitor xylose
1-phosphate utilizes many of the previously observed enzyme-ligand interactions.
In contrast, analysis of the ribose 1-phosphate complex reveals a combination of
new and conserved enzyme-ligand interactions for binding. The ability of PMM/PGM
to accommodate these two pentose phosphosugars in its active site may be
relevant for future efforts towards inhibitor design.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 PMM/PGM in complex with X1P and R1P. The protein is
colored by domain, with blue, light blue, pink and magenta for
domains 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively. (a) Ribbon diagram of
PMM/PGM with X1P (yellow) and R1P (green) bound in the active
site. (b) Superposition of the C^  atoms
of the R1P complex with those of apo-PMM/PGM (PDB code 1k2y )
shown in gray, demonstrating the rotation of domain 4. Close-up
view of the active site of PMM/PGM with bound (c) X1P and (d)
R1P. For clarity, only interactions between side chains of the
enzyme and ligands are highlighted; water molecules are shown as
spheres. (e) For comparison, a superposition of the slow
substrate R1P and a preferred substrate G1P (cyan) in the active
site of PMM/PGM is shown. atoms
of the R1P complex with those of apo-PMM/PGM (PDB code 1k2y )
shown in gray, demonstrating the rotation of domain 4. Close-up
view of the active site of PMM/PGM with bound (c) X1P and (d)
R1P. For clarity, only interactions between side chains of the
enzyme and ligands are highlighted; water molecules are shown as
spheres. (e) For comparison, a superposition of the slow
substrate R1P and a preferred substrate G1P (cyan) in the active
site of PMM/PGM is shown.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallograph Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
(2006,
62,
722-726)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

