 |
PDBsum entry 2fkf

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.2
- phosphoglucomutase (alpha-D-glucose-1,6-bisphosphate-dependent).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-glucose, UDP-galactose and UDP-glucuronate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 80.00% similarity
|
=
|
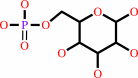 alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.8
- phosphomannomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate = D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 80.00% similarity
|
=
|
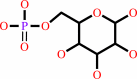 D-mannose 6-phosphate
D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:15564-15571
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The reaction of phosphohexomutase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: structural insights into a simple processive enzyme.
|
|
C.Regni,
A.M.Schramm,
L.J.Beamer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase (PMM/PGM) from Pseudomonas
aeruginosa catalyzes the reversible conversion of 1-phospho to 6-phospho-sugars.
The reaction entails two phosphoryl transfers, with an intervening 180 degrees
reorientation of the reaction intermediate (e.g. glucose 1,6-bisphosphate)
during catalysis. Reorientation of the intermediate occurs without dissociation
from the active site of the enzyme and is, thus, a simple example of
processivity, as defined by multiple rounds of catalysis without release of
substrate. Structural characterization of two PMM/PGM-intermediate complexes
with glucose 1,6-bisphosphate provides new insights into the reaction catalyzed
by the enzyme, including the reorientation of the intermediate. Kinetic analyses
of site-directed mutants prompted by the structural studies reveal active site
residues critical for maintaining association with glucose 1,6-bisphosphate
during its unique dynamic reorientation in the active site of PMM/PGM.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIGURE 2. The final 2 F[o] – F[c] maps (blue, contoured
at 1. 0  ) for G16P in the
dephospho-PMM/PGM·G16P complex (a) and
phospho-PMM/PGM·G16P complex (b). Electron density for
Arg-15 and Arg-20 is also shown for this complex. ) for G16P in the
dephospho-PMM/PGM·G16P complex (a) and
phospho-PMM/PGM·G16P complex (b). Electron density for
Arg-15 and Arg-20 is also shown for this complex.
|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. a, superposition of the protein backbones for
apo-PMM/PGM (Apo) and its complexes with G16P. DP,
dephospho-PMM/PGM; P, phospho-PMM/PGM. Domains 1–4 are shown
in green, yellow, red, and blue, respectively. G16P as bound to
phosphoenzyme is shown in magenta and to dephosphoenzyme is
shown in cyan. b, a close-up view of G16P in the active site of
the two PMM/PGM-intermediate complexes showing their different
relative binding positions. The protein backbone is shown in
solid (dephosphoenzyme) and semitransparent (phosphoenzyme).
Shown are hydrogen bonds between G16P and dephospho-PMM/PGM (c)
and phospho-PMM/PGM (d). Protein residues that contact the
intermediate are shown as sticks; water molecules are shown as
blue spheres.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
15564-15571)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Chu,
Q.C.Zheng,
X.Li,
Y.S.Zhao,
J.L.Zhang,
and
H.X.Zhang
(2011).
DFT investigation on the reaction mechanism catalyzed by α-phosphomannomutase1 in protonated/deprotonated states.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
17,
577-585.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Schramm,
D.Karr,
R.Mehra-Chaudhary,
S.R.Van Doren,
C.M.Furdui,
and
L.J.Beamer
(2010).
Breaking the covalent connection: Chain connectivity and the catalytic reaction of PMM/PGM.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
19,
1235-1242.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Y.Chuang,
R.Mehra-Chaudhary,
C.H.Ngan,
B.S.Zerbe,
D.Kozakov,
S.Vajda,
and
L.J.Beamer
(2010).
Domain motion and interdomain hot spots in a multidomain enzyme.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
19,
1662-1672.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mitra,
J.Cui,
P.W.Robbins,
and
J.Samuelson
(2010).
A deeply divergent phosphoglucomutase (PGM) of Giardia lamblia has both PGM and phosphomannomutase activities.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
20,
1233-1240.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Dai,
L.Finci,
C.Zhang,
S.Lahiri,
G.Zhang,
E.Peisach,
K.N.Allen,
and
D.Dunaway-Mariano
(2009).
Analysis of the structural determinants underlying discrimination between substrate and solvent in beta-phosphoglucomutase catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1984-1995.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Regni,
G.S.Shackelford,
and
L.J.Beamer
(2006).
Complexes of the enzyme phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase with a slow substrate and an inhibitor.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
722-726.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

