 |
PDBsum entry 2eab

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of 1,2-a-l-fucosidase from bifidobacterium bifidum (apo form)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Alpha-fucosidase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic domain, residues 0-898. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bifidobacterium bifidum. Organism_taxid: 1681. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.12Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.189
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Nagae,A.Tsuchiya,T.Katayama,K.Yamamoto,S.Wakatsuki,R.Kato
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.Nagae
et al.
(2007).
Structural basis on the catalytic reaction mechanism of novel 1,2-alpha-L-fucosidase (AFCA) from Bifidobacterium bifidum.
J Biol Chem,
282,
18497-18509.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
31-Jan-07
|
Release date:
|
24-Apr-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q6JV24
(Q6JV24_BIFBI) -
Alpha-fucosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1959 a.a.
888 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.1.63
- 1,2-alpha-L-fucosidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
methyl-2-alpha-L-fucopyranosyl-beta-D-galactoside + H2O = methyl beta-D- galactoside + L-fucose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
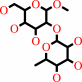 methyl-2-alpha-L-fucopyranosyl-beta-D-galactoside
methyl-2-alpha-L-fucopyranosyl-beta-D-galactoside
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
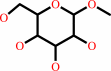 methyl beta-D- galactoside
methyl beta-D- galactoside
|
+
|
 L-fucose
L-fucose
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
282:18497-18509
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis on the catalytic reaction mechanism of novel 1,2-alpha-L-fucosidase (AFCA) from Bifidobacterium bifidum.
|
|
M.Nagae,
A.Tsuchiya,
T.Katayamka,
K.Yamamoto,
S.Wakatsuki,
R.Kato.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
1,2-alpha-L-Fucosidase (AfcA), which hydrolyzes the glycosidic linkage of
Fucalpha1-2Gal via an inverting mechanism, was recently isolated from
Bifidobacterium bifidum and classified as the first member of the novel
glycoside hydrolase family 95 (GH95). To better understand the molecular
mechanism of this enzyme, we determined the X-ray crystal structures of the AfcA
catalytic (Fuc) domain in unliganded and complexed forms with
deoxyfuconojirimycin (inhibitor), 2'-fucosyllactose (substrate), and
L-fucose and lactose (products) at 1.12-2.10 A resolution. The AfcA Fuc domain
is composed of four regions, an N-terminal beta region, a helical linker, an
(alpha/alpha)6 helical barrel domain, and a C-terminal beta region, and this
arrangement is similar to bacterial phosphorylases. In the complex structures,
the ligands were buried in the central cavity of the helical barrel domain.
Structural analyses in combination with mutational experiments revealed that the
highly conserved Glu566 likely acts as a general acid catalyst. However, no
carboxylic acid residue is found at the appropriate position for a general base
catalyst. Instead, a water molecule stabilized by Asn423 in the substrate-bound
complex is suitably located to perform a nucleophilic attack on the C1 atom of
L-fucose moiety in 2'-fucosyllactose, and its location is nearly identical
near the O1 atom of beta-L-fucose in the products-bound complex. Based on these
data, we propose and discuss a novel catalytic reaction mechanism of AfcA.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIGURE 1. Crystal structure of B. bifidum AfcA fucosidase
catalytic domain (Fuc domain). a, ribbon model of the Fuc domain
is shown. The N-terminal  region, helical linker
region, central helical barrel domain, and C-terminal region, helical linker
region, central helical barrel domain, and C-terminal  region
are colored in blue, cyan, yellow, and red, respectively. b,
electrostatic surface potential map of the Fuc domain. Positive
(blue) and negative (red) potentials are mapped on the van der
Waals surfaces in the range -10 K[b]T (red) to +10 K[b]T (blue),
where K[b] is Boltzmann's constant and T is the absolute
temperature. region
are colored in blue, cyan, yellow, and red, respectively. b,
electrostatic surface potential map of the Fuc domain. Positive
(blue) and negative (red) potentials are mapped on the van der
Waals surfaces in the range -10 K[b]T (red) to +10 K[b]T (blue),
where K[b] is Boltzmann's constant and T is the absolute
temperature.
|
 |
Figure 6.
FIGURE 6. Proposed catalytic reaction mechanism of the AfcA
fucosidase. Hydrogen bonds are depicted by dotted lines. The
directions of nucleophilic attack and proton donation are
indicated by blank arrows.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2007,
282,
18497-18509)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Zivkovic,
J.B.German,
C.B.Lebrilla,
and
D.A.Mills
(2011).
Human milk glycobiome and its impact on the infant gastrointestinal microbiota.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
4653-4658.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kiyohara,
K.Tanigawa,
T.Chaiwangsri,
T.Katayama,
H.Ashida,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2011).
An exo-{alpha}-sialidase from bifidobacteria involved in the degradation of sialyloligosaccharides in human milk and intestinal glycoconjugates.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
21,
437-447.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Turroni,
F.Bottacini,
E.Foroni,
I.Mulder,
J.H.Kim,
A.Zomer,
B.Sánchez,
A.Bidossi,
A.Ferrarini,
V.Giubellini,
M.Delledonne,
B.Henrissat,
P.Coutinho,
M.Oggioni,
G.F.Fitzgerald,
D.Mills,
A.Margolles,
D.Kelly,
D.van Sinderen,
and
M.Ventura
(2010).
Genome analysis of Bifidobacterium bifidum PRL2010 reveals metabolic pathways for host-derived glycan foraging.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
19514-19519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hidaka,
S.Fushinobu,
Y.Honda,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2010).
Structural explanation for the acquisition of glycosynthase activity.
|
| |
J Biochem,
147,
237-244.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Miwa,
T.Horimoto,
M.Kiyohara,
T.Katayama,
M.Kitaoka,
H.Ashida,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2010).
Cooperation of β-galactosidase and β-N-acetylhexosaminidase from bifidobacteria in assimilation of human milk oligosaccharides with type 2 structure.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
20,
1402-1409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fushinobu
(2010).
Unique sugar metabolic pathways of bifidobacteria.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
74,
2374-2384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.V.Vuong,
and
D.B.Wilson
(2010).
Glycoside hydrolases: catalytic base/nucleophile diversity.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
107,
195-205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Dodd,
S.A.Kocherginskaya,
M.A.Spies,
K.E.Beery,
C.A.Abbas,
R.I.Mackie,
and
I.K.Cann
(2009).
Biochemical analysis of a beta-D-xylosidase and a bifunctional xylanase-ferulic acid esterase from a xylanolytic gene cluster in Prevotella ruminicola 23.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
3328-3338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ashida,
A.Miyake,
M.Kiyohara,
J.Wada,
E.Yoshida,
H.Kumagai,
T.Katayama,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2009).
Two distinct alpha-L-fucosidases from Bifidobacterium bifidum are essential for the utilization of fucosylated milk oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
19,
1010-1017.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kiyohara,
A.Tachizawa,
M.Nishimoto,
M.Kitaoka,
H.Ashida,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2009).
Prebiotic effect of lacto-N-biose I on bifidobacterial growth.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
73,
1175-1179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nakajima,
M.Nishimoto,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2009).
Characterization of three beta-galactoside phosphorylases from Clostridium phytofermentans: discovery of d-galactosyl-beta1->4-l-rhamnose phosphorylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19220-19227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ishida,
S.Fushinobu,
R.Kawai,
M.Kitaoka,
K.Igarashi,
and
M.Samejima
(2009).
Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 55 {beta}-1,3-glucanase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
10100-10109.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.V.Vuong,
and
D.B.Wilson
(2009).
The absence of an identifiable single catalytic base residue in Thermobifida fusca exocellulase Cel6B.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
3837-3845.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Vocadlo,
and
G.J.Davies
(2008).
Mechanistic insights into glycosidase chemistry.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
539-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wada,
T.Ando,
M.Kiyohara,
H.Ashida,
M.Kitaoka,
M.Yamaguchi,
H.Kumagai,
T.Katayama,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2008).
Bifidobacterium bifidum lacto-N-biosidase, a critical enzyme for the degradation of human milk oligosaccharides with a type 1 structure.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
74,
3996-4004.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Ruas-Madiedo,
M.Gueimonde,
M.Fernández-García,
C.G.de los Reyes-Gavilán,
and
A.Margolles
(2008).
Mucin degradation by Bifidobacterium strains isolated from the human intestinal microbiota.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
74,
1936-1940.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

