
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Protein transport
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human rab11 in complex with fip3 rab-binding domain
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ras-related protein rab-11a. Chain: a, b. Fragment: residues 7-173. Synonym: rab-11. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Rab11 family-interacting protein 3. Chain: c, d. Fragment: rab-binding domain.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.202
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Shiba,H.Koga,H.W.Shin,M.Kawasaki,R.Kato,K.Nakayama,S.Wakatsuki
|
Key ref:

|
 |
T.Shiba
et al.
(2006).
Structural basis for Rab11-dependent membrane recruitment of a family of Rab11-interacting protein 3 (FIP3)/Arfophilin-1.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
15416-15421.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
26-Sep-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
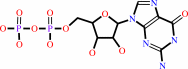 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
103:15416-15421
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for Rab11-dependent membrane recruitment of a family of Rab11-interacting protein 3 (FIP3)/Arfophilin-1.
|
|
T.Shiba,
H.Koga,
H.W.Shin,
M.Kawasaki,
R.Kato,
K.Nakayama,
S.Wakatsuki.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Family of Rab11-interacting protein (FIP)3/Arfophlin-1 and FIP4/Arfophilin-2 are
dual effectors for Rab11 and ADP ribosylation factor (ARF)5/ARF6, which are
involved in membrane delivery from recycling endosomes to the plasma membrane
during cytokinesis. Here, we define the distinct C-terminal binding regions of
FIP3 and FIP4 for Rab11 and ARF5/ARF6. Furthermore, we determined the crystal
structure of Rab11 in complex with the Rab11-binding domain (RBD) of FIP3. The
long amphiphilic alpha-helix of FIP3-RBD forms a parallel coiled-coil homodimer,
with two symmetric interfaces with two Rab11 molecules. The hydrophobic side of
the RBD helix is involved in homodimerization and mediates the interaction with
the Rab11 switch 1 region, whereas the opposite hydrophilic side interacts with
the Rab11 switch 2 and is the major factor contributing to the binding
specificity. The bivalent interaction of FIP3 with Rab11 at the C terminus
allows FIP3 to coordinately function with other binding partners, including ARFs.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Superposition of Rab11 in different forms. The
switch 1 and switch 2 regions are shown. The side chains of
Arg-72 and Arg-74 in the switch 2 region are indicated by
ball-and-stick models. GTP/GDP molecules also are presented as
ball-and-stick models. The GDP-bound form (PDB ID code 1OIV) is
blue, the GTP-bound free form (PDB ID code 1OIW) is green, and
molecule A GTP-bound Rab11 in complex with FIP3-RBD is red,
whereas molecule B is orange.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Fig. 6. Interaction between Rab11 and FIP3-RBD. Shown are
close-up views of the switch 1 (a), switch 2 (b), and
interswitch (c) regions of Rab11 in complex with FIP3-RBD. The
color scheme is the same as that of Fig. 3b. Residues involved
in the interaction are labeled and indicated by ball-and-stick
models. The cyan dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds or
electrostatic interactions.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Mishra,
S.Eathiraj,
S.Corvera,
and
D.G.Lambright
(2010).
Structural basis for Rab GTPase recognition and endosome tethering by the C2H2 zinc finger of Early Endosomal Autoantigen 1 (EEA1).
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
10866-10871.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yamamoto,
H.Koga,
Y.Katoh,
S.Takahashi,
K.Nakayama,
and
H.W.Shin
(2010).
Functional cross-talk between Rab14 and Rab4 through a dual effector, RUFY1/Rabip4.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
21,
2746-2755.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.de Vries,
A.S.Melquiond,
P.L.Kastritis,
E.Karaca,
A.Bordogna,
M.van Dijk,
J.P.Rodrigues,
and
A.M.Bonvin
(2010).
Strengths and weaknesses of data-driven docking in critical assessment of prediction of interactions.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
3242-3249.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jing,
E.Tarbutton,
G.Wilson,
and
R.Prekeris
(2009).
Rab11-FIP3 is a Rab11-binding protein that regulates breast cancer cell motility by modulating the actin cytoskeleton.
|
| |
Eur J Cell Biol,
88,
325-341.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Mazelova,
L.Astuto-Gribble,
H.Inoue,
B.M.Tam,
E.Schonteich,
R.Prekeris,
O.L.Moritz,
P.A.Randazzo,
and
D.Deretic
(2009).
Ciliary targeting motif VxPx directs assembly of a trafficking module through Arf4.
|
| |
EMBO J,
28,
183-192.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wei,
Y.Liu,
K.Bose,
G.D.Henry,
and
J.D.Baleja
(2009).
Disorder and structure in the Rab11 binding domain of Rab11 family interacting protein 2.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
549-557.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Lee,
A.Mishra,
and
D.G.Lambright
(2009).
Structural mechanisms for regulation of membrane traffic by rab GTPases.
|
| |
Traffic,
10,
1377-1389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Khandelwal,
S.N.Abraham,
and
G.Apodaca
(2009).
Cell biology and physiology of the uroepithelium.
|
| |
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol,
297,
F1477-F1501.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Recacha,
A.Boulet,
F.Jollivet,
S.Monier,
A.Houdusse,
B.Goud,
and
A.R.Khan
(2009).
Structural basis for recruitment of Rab6-interacting protein 1 to Golgi via a RUN domain.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
21-30.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Isabet,
G.Montagnac,
K.Regazzoni,
B.Raynal,
F.El Khadali,
P.England,
M.Franco,
P.Chavrier,
A.Houdusse,
and
J.Ménétrey
(2009).
The structural basis of Arf effector specificity: the crystal structure of ARF6 in a complex with JIP4.
|
| |
EMBO J,
28,
2835-2845.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.An,
C.Y.Chen,
B.Moyer,
P.Rotkiewicz,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.Godzik,
I.A.Wilson,
and
W.E.Balch
(2009).
Structural and functional analysis of the globular head domain of p115 provides insight into membrane tethering.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
391,
26-41.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Burguete,
T.D.Fenn,
A.T.Brunger,
and
S.R.Pfeffer
(2008).
Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of the golgin GCC185.
|
| |
Cell,
132,
286-298.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.C.Simon,
E.Schonteich,
C.C.Wu,
A.Piekny,
D.Ekiert,
X.Yu,
G.W.Gould,
M.Glotzer,
and
R.Prekeris
(2008).
Sequential Cyk-4 binding to ECT2 and FIP3 regulates cleavage furrow ingression and abscission during cytokinesis.
|
| |
EMBO J,
27,
1791-1803.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Inoue,
V.L.Ha,
R.Prekeris,
and
P.A.Randazzo
(2008).
Arf GTPase-activating protein ASAP1 interacts with Rab11 effector FIP3 and regulates pericentrosomal localization of transferrin receptor-positive recycling endosome.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
19,
4224-4237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Yousef,
H.Kamikubo,
M.Kataoka,
R.Kato,
and
S.Wakatsuki
(2008).
Miranda cargo-binding domain forms an elongated coiled-coil homodimer in solution: implications for asymmetric cell division in Drosophila.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
908-917.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Westlake,
J.R.Junutula,
G.C.Simon,
M.Pilli,
R.Prekeris,
R.H.Scheller,
P.K.Jackson,
and
A.G.Eldridge
(2007).
Identification of Rab11 as a small GTPase binding protein for the Evi5 oncogene.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
1236-1241.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.P.Horgan,
A.Oleksy,
A.V.Zhdanov,
P.Y.Lall,
I.J.White,
A.R.Khan,
C.E.Futter,
J.G.McCaffrey,
and
M.W.McCaffrey
(2007).
Rab11-FIP3 is critical for the structural integrity of the endosomal recycling compartment.
|
| |
Traffic,
8,
414-430.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Pincet
(2007).
Membrane recruitment of scaffold proteins drives specific signaling.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
2,
e977.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

