 |
PDBsum entry 1vst

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.9
- uracil phosphoribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
UMP + diphosphate = 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate + uracil
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
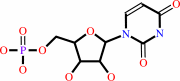 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.61% similarity
|
=
|
5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
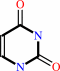 uracil
uracil
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
393:464-477
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and kinetic studies of the allosteric transition in Sulfolobus solfataricus uracil phosphoribosyltransferase: Permanent activation by engineering of the C-terminus.
|
|
S.Christoffersen,
A.Kadziola,
E.Johansson,
M.Rasmussen,
M.Willemoës,
K.F.Jensen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Uracil phosphoribosyltransferase catalyzes the conversion of
5-phosphoribosyl-alpha-1-diphosphate (PRPP) and uracil to uridine monophosphate
(UMP) and diphosphate (PP(i)). The tetrameric enzyme from Sulfolobus
solfataricus has a unique type of allosteric regulation by cytidine triphosphate
(CTP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). Here we report two structures of the
activated state in complex with GTP. One structure (refined at 2.8-A resolution)
contains PRPP in all active sites, while the other structure (refined at 2.9-A
resolution) has PRPP in two sites and the hydrolysis products,
ribose-5-phosphate and PP(i), in the other sites. Combined with three existing
structures of uracil phosphoribosyltransferase in complex with UMP and the
allosteric inhibitor cytidine triphosphate (CTP), these structures provide
valuable insight into the mechanism of allosteric transition from inhibited to
active enzyme. The regulatory triphosphates bind at a site in the center of the
tetramer in a different manner and change the quaternary arrangement. Both
effectors contact Pro94 at the beginning of a long beta-strand in the dimer
interface, which extends into a flexible loop over the active site. In the
GTP-bound state, two flexible loop residues, Tyr123 and Lys125, bind the PP(i)
moiety of PRPP in the neighboring subunit and contribute to catalysis, while in
the inhibited state, they contribute to the configuration of the active site for
UMP rather than PRPP binding. The C-terminal Gly216 participates in a
hydrogen-bond network in the dimer interface that stabilizes the inhibited, but
not the activated, state. Tagging the C-terminus with additional amino acids
generates an endogenously activated enzyme that binds GTP without effects on
activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

