 |
PDBsum entry 1vot

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.7
- acetylcholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
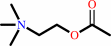 acetylcholine
acetylcholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
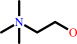 choline
choline
|
+
|
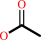 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Struct Biol
4:57-63
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid, (-)-huperzine A.
|
|
M.L.Raves,
M.Harel,
Y.P.Pang,
I.Silman,
A.P.Kozikowski,
J.L.Sussman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
(-)-Huperzine A (HupA) is found in an extract from a club moss that has been
used for centuries in Chinese folk medicine. Its action has been attributed to
its ability to strongly inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The crystal
structure of the complex of AChE with optically pure HupA at 2.5 A resolution
shows an unexpected orientation for the inhibitor with surprisingly few strong
direct interactions with protein residues to explain its high affinity. This
structure is compared to the native structure of AChE devoid of any inhibitor as
determined to the same resolution. An analysis of the affinities of structural
analogues of HupA, correlated with their interactions with the protein, shows
the importance of individual hydrophobic interactions between HupA and aromatic
residues in the active-site gorge of AChE.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.Kitisripanya,
P.Saparpakorn,
P.Wolschann,
and
S.Hannongbua
(2011).
Binding of huperzine A and galanthamine to acetylcholinesterase, based on ONIOM method.
|
| |
Nanomedicine,
7,
60-68.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Jin,
L.Yang,
S.J.Liu,
J.Wang,
S.Li,
H.Q.Lin,
D.C.Wan,
and
C.Hu
(2010).
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3,6-diaryl-7H-thiazolo[3,2-b] [1,2,4]triazin-7-one derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
|
| |
Arch Pharm Res,
33,
1641-1649.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Ekström,
A.Hörnberg,
E.Artursson,
L.G.Hammarström,
G.Schneider,
and
Y.P.Pang
(2009).
Structure of HI-6*sarin-acetylcholinesterase determined by X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulation: reactivator mechanism and design.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e5957.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Mihailescu,
and
H.Meirovitch
(2009).
Absolute free energy and entropy of a mobile loop of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
J Phys Chem B,
113,
7950-7964.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Aracava,
E.F.Pereira,
M.Akkerman,
M.Adler,
and
E.X.Albuquerque
(2009).
Effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine, and (+/-)huperzine A in counteracting the acute toxicity of organophosphorus nerve agents: comparison with galantamine.
|
| |
J Pharmacol Exp Ther,
331,
1014-1024.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.P.Pang,
F.Ekström,
G.A.Polsinelli,
Y.Gao,
S.Rana,
D.H.Hua,
B.Andersson,
P.O.Andersson,
L.Peng,
S.K.Singh,
R.K.Mishra,
K.Y.Zhu,
A.M.Fallon,
D.W.Ragsdale,
and
S.Brimijoin
(2009).
Selective and irreversible inhibitors of mosquito acetylcholinesterases for controlling malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e6851.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.P.Pang,
S.K.Singh,
Y.Gao,
T.L.Lassiter,
R.K.Mishra,
K.Y.Zhu,
and
S.Brimijoin
(2009).
Selective and irreversible inhibitors of aphid acetylcholinesterases: steps toward human-safe insecticides.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
4,
e4349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Shafferman,
D.Barak,
D.Stein,
C.Kronman,
B.Velan,
N.H.Greig,
and
A.Ordentlich
(2008).
Flexibility versus "rigidity" of the functional architecture of AChE active center.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
175,
166-172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Coleman,
R.H.Ratcliffe,
S.A.Oguntayo,
X.Shi,
B.P.Doctor,
R.K.Gordon,
and
M.P.Nambiar
(2008).
[+]-Huperzine A treatment protects against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
175,
387-395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Zhang,
C.Y.Zheng,
H.Yan,
Z.F.Wang,
L.L.Tang,
X.Gao,
and
X.C.Tang
(2008).
Potential therapeutic targets of huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
175,
396-402.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Zhang,
H.Yan,
and
X.C.Tang
(2008).
Non-cholinergic effects of huperzine A: beyond inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
Cell Mol Neurobiol,
28,
173-183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.T.Little,
S.Walsh,
and
P.S.Aisen
(2008).
An update on huperzine A as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
|
| |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs,
17,
209-215.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Ruan,
Z.Yang,
and
M.T.Rodgers
(2007).
Influence of the d orbital occupation on the nature and strength of copper cation-pi interactions: threshold collision-induced dissociation and theoretical studies.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
9,
5902-5918.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Ekström,
C.Astot,
and
Y.P.Pang
(2007).
Novel nerve-agent antidote design based on crystallographic and mass spectrometric analyses of tabun-conjugated acetylcholinesterase in complex with antidotes.
|
| |
Clin Pharmacol Ther,
82,
282-293.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Stöckigt,
and
S.Panjikar
(2007).
Structural biology in plant natural product biosynthesis--architecture of enzymes from monoterpenoid indole and tropane alkaloid biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
1382-1400.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.L.Shen,
G.X.Liu,
and
Y.Tang
(2007).
Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies of 2-substituted 1-indanone derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
28,
2053-2063.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Wang,
and
Y.P.Pang
(2007).
Accurate reproduction of 161 small-molecule complex crystal structures using the EUDOC program: expanding the use of EUDOC to supramolecular chemistry.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
2,
e531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rana,
B.Kundu,
and
S.Durani
(2007).
A mixed-alpha,beta miniprotein stereochemically reprogrammed to high-binding affinity for acetylcholine.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
87,
231-243.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Pastorin,
S.Marchesan,
J.Hoebeke,
T.Da Ros,
L.Ehret-Sabatier,
J.P.Briand,
M.Prato,
and
A.Bianco
(2006).
Design and activity of cationic fullerene derivatives as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
4,
2556-2562.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Bui,
and
J.A.McCammon
(2006).
Protein complex formation by acetylcholinesterase and the neurotoxin fasciculin-2 appears to involve an induced-fit mechanism.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
15451-15456.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Xie,
Y.Tang,
W.Li,
X.H.Wang,
and
Z.B.Qiu
(2006).
Investigation of the binding mode of (-)-meptazinol and bis-meptazinol derivatives on acetylcholinesterase using a molecular docking method.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
12,
390-397.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Wang,
H.Yan,
and
X.C.Tang
(2006).
Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
27,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Bourne,
Z.Radic,
G.Sulzenbacher,
E.Kim,
P.Taylor,
and
P.Marchot
(2006).
Substrate and product trafficking through the active center gorge of acetylcholinesterase analyzed by crystallography and equilibrium binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
29256-29267.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.P.Pang
(2006).
Novel acetylcholinesterase target site for malaria mosquito control.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
1,
e58.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Q.Liang,
and
X.C.Tang
(2006).
Comparative studies of huperzine A, donepezil, and rivastigmine on brain acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in freely-moving rats.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
27,
1127-1136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.K.Manojkumar,
C.Cui,
and
K.S.Kim
(2005).
Theoretical insights into the mechanism of acetylcholinesterase-catalyzed acylation of acetylcholine.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
26,
606-611.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Umezawa,
and
M.Nishio
(2005).
CH/pi hydrogen bonds as evidenced in the substrate specificity of acetylcholine esterase.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
79,
248-258.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Berchanski,
B.Shapira,
and
M.Eisenstein
(2004).
Hydrophobic complementarity in protein-protein docking.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
130-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Weik,
X.Vernede,
A.Royant,
and
D.Bourgeois
(2004).
Temperature derivative fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool to study dynamical changes in protein crystals.
|
| |
Biophys J,
86,
3176-3185.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Fletcher,
B.C.Geyer,
A.Smith,
T.Evron,
L.Joshi,
H.Soreq,
and
T.S.Mor
(2004).
Tissue distribution of cholinesterases and anticholinesterases in native and transgenic tomato plants.
|
| |
Plant Mol Biol,
55,
33-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Saxena,
J.M.Fedorko,
C.R.Vinayaka,
R.Medhekar,
Z.Radić,
P.Taylor,
O.Lockridge,
and
B.P.Doctor
(2003).
Aromatic amino-acid residues at the active and peripheral anionic sites control the binding of E2020 (Aricept) to cholinesterases.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
4447-4458.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Ben-Zeev,
and
M.Eisenstein
(2003).
Weighted geometric docking: incorporating external information in the rotation-translation scan.
|
| |
Proteins,
52,
24-27.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Johnson,
B.Cusack,
T.F.Hughes,
E.H.McCullough,
A.Fauq,
P.Romanovskis,
A.F.Spatola,
and
T.L.Rosenberry
(2003).
Inhibitors tethered near the acetylcholinesterase active site serve as molecular rulers of the peripheral and acylation sites.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
38948-38955.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Shi,
K.Tai,
J.A.McCammon,
P.Taylor,
and
D.A.Johnson
(2003).
Nanosecond dynamics of the mouse acetylcholinesterase cys69-cys96 omega loop.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
30905-30911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Bourne,
P.Taylor,
Z.Radić,
and
P.Marchot
(2003).
Structural insights into ligand interactions at the acetylcholinesterase peripheral anionic site.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
1.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Heifetz,
E.Katchalski-Katzir,
and
M.Eisenstein
(2002).
Electrostatics in protein-protein docking.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
571-587.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Nachon,
Y.Nicolet,
N.Viguié,
P.Masson,
J.C.Fontecilla-Camps,
and
O.Lockridge
(2002).
Engineering of a monomeric and low-glycosylated form of human butyrylcholinesterase: expression, purification, characterization and crystallization.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
630-637.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Dvir,
D.M.Wong,
M.Harel,
X.Barril,
M.Orozco,
F.J.Luque,
D.Muñoz-Torrero,
P.Camps,
T.L.Rosenberry,
I.Silman,
and
J.L.Sussman
(2002).
3D structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase complexed with huprine X at 2.1 A resolution: kinetic and molecular dynamic correlates.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
2970-2981.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Shi,
Z.Radic',
and
P.Taylor
(2002).
Inhibitors of different structure induce distinguishing conformations in the omega loop, Cys69-Cys96, of mouse acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
43301-43308.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Shi,
A.E.Boyd,
Z.Radic,
and
P.Taylor
(2001).
Reversibly bound and covalently attached ligands induce conformational changes in the omega loop, Cys69-Cys96, of mouse acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
42196-42204.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Weik,
R.B.Ravelli,
I.Silman,
J.L.Sussman,
P.Gros,
and
J.Kroon
(2001).
Specific protein dynamics near the solvent glass transition assayed by radiation-induced structural changes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
1953-1961.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.P.Pang,
E.Perola,
K.Xu,
and
F.G.Prendergast
(2001).
EUDOC: a computer program for identification of drug interaction sites in macromolecules and drug leads from chemical databases.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
22,
1750-1771.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Tsigelny,
I.N.Shindyalov,
P.E.Bourne,
T.C.Südhof,
and
P.Taylor
(2000).
Common EF-hand motifs in cholinesterases and neuroligins suggest a role for Ca2+ binding in cell surface associations.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
180-185.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chang
(2000).
Medicinal herbs: drugs or dietary supplements?
|
| |
Biochem Pharmacol,
59,
211-219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Harel,
G.Kryger,
T.L.Rosenberry,
W.D.Mallender,
T.Lewis,
R.J.Fletcher,
J.M.Guss,
I.Silman,
and
J.L.Sussman
(2000).
Three-dimensional structures of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase and of its complexes with two potent inhibitors.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1063-1072.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Weik,
R.B.Ravelli,
G.Kryger,
S.McSweeney,
M.L.Raves,
M.Harel,
P.Gros,
I.Silman,
J.Kroon,
and
J.L.Sussman
(2000).
Specific chemical and structural damage to proteins produced by synchrotron radiation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
623-628.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.B.Ravelli,
and
S.M.McSweeney
(2000).
The 'fingerprint' that X-rays can leave on structures.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
315-328.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ordentlich,
D.Barak,
C.Kronman,
H.P.Benschop,
L.P.De Jong,
N.Ariel,
R.Barak,
Y.Segall,
B.Velan,
and
A.Shafferman
(1999).
Exploring the active center of human acetylcholinesterase with stereomers of an organophosphorus inhibitor with two chiral centers.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
3055-3066.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.B.Millard,
G.Kryger,
A.Ordentlich,
H.M.Greenblatt,
M.Harel,
M.L.Raves,
Y.Segall,
D.Barak,
A.Shafferman,
I.Silman,
and
J.L.Sussman
(1999).
Crystal structures of aged phosphonylated acetylcholinesterase: nerve agent reaction products at the atomic level.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
7032-7039.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Bartolucci,
E.Perola,
L.Cellai,
M.Brufani,
and
D.Lamba
(1999).
"Back door" opening implied by the crystal structure of a carbamoylated acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5714-5719.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Zeng,
H.Jiang,
Y.Zhai,
H.Zhang,
K.Chen,
and
R.Ji
(1999).
Synthesis and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of huperzine A-E2020 combined compound.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
9,
3279-3284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kryger,
I.Silman,
and
J.L.Sussman
(1999).
Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
297-307.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Chen,
Y.L.Luo,
M.J.Hwang,
F.C.Peng,
and
K.H.Ling
(1999).
Territrem B, a tremorgenic mycotoxin that inhibits acetylcholinesterase with a noncovalent yet irreversible binding mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
34916-34923.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Heikinheimo,
A.Goldman,
C.Jeffries,
and
D.L.Ollis
(1999).
Of barn owls and bankers: a lush variety of alpha/beta hydrolases.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
R141-R146.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tara,
T.P.Straatsma,
and
J.A.McCammon
(1999).
Mouse acetylcholinesterase unliganded and in complex with huperzine A: a comparison of molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
50,
35-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tara,
V.Helms,
T.P.Straatsma,
and
J.A.McCammon
(1999).
Molecular dynamics of mouse acetylcholinesterase complexed with huperzine A.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
50,
347-359.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Bourne,
P.Taylor,
P.E.Bougis,
and
P.Marchot
(1999).
Crystal structure of mouse acetylcholinesterase. A peripheral site-occluding loop in a tetrameric assembly.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
2963-2970.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ordentlich,
D.Barak,
C.Kronman,
N.Ariel,
Y.Segall,
B.Velan,
and
A.Shafferman
(1998).
Functional characteristics of the oxyanion hole in human acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
19509-19517.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Zeng,
H.Jiang,
X.Tang,
K.Chen,
and
R.Ji
(1998).
Synthesis and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of (+/-)-14-fluorohuperzine A.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
8,
1661-1664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.McCammon
(1998).
Theory of biomolecular recognition.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
245-249.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Chen,
L.J.Miercke,
J.Krucinski,
J.R.Starr,
G.Saenz,
X.Wang,
C.A.Spilburg,
L.G.Lange,
J.L.Ellsworth,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1998).
Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 A: novel structural features involved in lipase activation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
5107-5117.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.McFail-Isom,
X.Shui,
and
L.D.Williams
(1998).
Divalent cations stabilize unstacked conformations of DNA and RNA by interacting with base pi systems.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
17105-17111.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Williamson,
G.Gröbner,
P.J.Spooner,
K.W.Miller,
and
A.Watts
(1998).
Probing the agonist binding pocket in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a high-resolution solid-state NMR approach.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
10854-10859.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Szegletes,
W.D.Mallender,
and
T.L.Rosenberry
(1998).
Nonequilibrium analysis alters the mechanistic interpretation of inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by peripheral site ligands.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
4206-4216.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

