 |
PDBsum entry 1vkj

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.8.2.23
- [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 1.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n) + 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate = 3-sulfo-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n) + adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n)
|
+
|
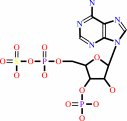 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate
3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate
|
=
|
3-sulfo-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n)
|
+
|
adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:25789-25797
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure and mutational analysis of heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 1.
|
|
S.C.Edavettal,
K.A.Lee,
M.Negishi,
R.J.Linhardt,
J.Liu,
L.C.Pedersen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Heparan sulfate interacts with antithrombin, a protease inhibitor, to regulate
blood coagulation. Heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 1 performs the
crucial last step modification in the biosynthesis of anticoagulant heparan
sulfate. This enzyme transfers the sulfuryl group (SO(3)) from
3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate to the 3-OH position of a glucosamine
residue to form the 3-O-sulfo glucosamine, a structural motif critical for
binding of heparan sulfate to antithrombin. In this study, we report the crystal
structure of 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 1 at 2.5-A resolution in a binary
complex with 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate. This structure reveals residues
critical for 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binding and suggests residues
required for the binding of heparan sulfate. In addition, site-directed
mutagenesis analyses suggest that residues Arg-67, Lys-68, Arg-72, Glu-90,
His-92, Asp-95, Lys-123, and Arg-276 are essential for enzymatic activity. Among
these essential amino acid residues, we find that residues Arg-67, Arg-72,
His-92, and Asp-95 are conserved in heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferases but
not in heparan N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase, suggesting a role for these
residues in conferring substrate specificity. Results from this study provide
information essential for understanding the biosynthesis of anticoagulant
heparan sulfate and the general mechanism of action of heparan sulfate
sulfotransferases.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIG. 1. The schematic biosynthesis of anticoagulant heparan
sulfate. Five steps are involved in the biosynthesis of HS after
the polysaccharide backbone is made. The numbers indicate the
positions of each sugar unit. Both
N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase and C[5]-epimerase
modifications are indicated in red. The 2-O-sulfotransferase and
6-O-sulfotransferase modifications are indicated in black and
blue, respectively. The 3-O-sulfotransferase modification is
indicated in purple. For clarity, we have indicated the
3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 1 modifications only in this
figure. GlcUA, glucuronic; IdoUA, iduronic acid; Glc,
glucosamine.
|
 |
Figure 5.
FIG. 5. Charged surface diagram of the proposed heparan
binding cleft of the sulfotransferase domains of NST-1 (a) and
3-OST-1 (b). The global position of the cleft is marked with a
green dashed line. Blue surfaces signify positive charge,
whereas red surfaces signify negative charge. The double-sided
dash arrows (in green) indicate the region where HS may bind.
This figure was created using Swiss PDB viewer.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
25789-25797)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Danan,
Z.Yu,
P.J.Ludden,
W.Jia,
K.L.Moore,
and
J.A.Leary
(2010).
Catalytic mechanism of Golgi-resident human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2: a mass spectrometry approach.
|
| |
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,
21,
1633-1642.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.G.Martin,
M.Gupta,
Y.Xu,
S.Akella,
J.Liu,
J.S.Dordick,
and
R.J.Linhardt
(2009).
Toward an artificial Golgi: redesigning the biological activities of heparan sulfate on a digital microfluidic chip.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
11041-11048.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Peterson,
A.Frick,
and
J.Liu
(2009).
Design of biologically active heparan sulfate and heparin using an enzyme-based approach.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
26,
610-627.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Tyapochkin,
P.F.Cook,
and
G.Chen
(2008).
Isotope exchange at equilibrium indicates a steady state ordered kinetic mechanism for human sulfotransferase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
11894-11899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.N.Bethea,
D.Xu,
J.Liu,
and
L.C.Pedersen
(2008).
Redirecting the substrate specificity of heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase by structurally guided mutagenesis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
18724-18729.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Bojarová,
and
S.J.Williams
(2008).
Sulfotransferases, sulfatases and formylglycine-generating enzymes: a sulfation fascination.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
573-581.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chen,
C.L.Jones,
and
J.Liu
(2007).
Using an enzymatic combinatorial approach to identify anticoagulant heparan sulfate structures.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
14,
986-993.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Liu,
and
L.C.Pedersen
(2007).
Anticoagulant heparan sulfate: structural specificity and biosynthesis.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
74,
263-272.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Sasisekharan,
R.Raman,
and
V.Prabhakar
(2006).
Glycomics approach to structure-function relationships of glycosaminoglycans.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biomed Eng,
8,
181-231.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Mougous,
C.J.Petzold,
R.H.Senaratne,
D.H.Lee,
D.L.Akey,
F.L.Lin,
S.E.Munchel,
M.R.Pratt,
L.W.Riley,
J.A.Leary,
J.M.Berger,
and
C.R.Bertozzi
(2004).
Identification, function and structure of the mycobacterial sulfotransferase that initiates sulfolipid-1 biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
721-729.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.L.Rath,
D.Verdugo,
and
S.Hemmerich
(2004).
Sulfotransferase structural biology and inhibitor discovery.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
9,
1003-1011.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

