 |
PDBsum entry 1vj3

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1vj3
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural studies on bio-active compounds. Crystal structure and molecular modeling studies on the pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase cofactor complex with tab, a highly selective antifolate.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Dihydrofolate reductase. Chain: a. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pneumocystis carinii. Organism_taxid: 4754. Gene: c-DNA p.Carinii dhfr. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
V.Cody,N.Galitsky,D.Rak,J.R.Luft,S.F.Queener,C.A.Laughton,F.G.Malcolm
|
Key ref:

|
 |
V.Cody
et al.
(2000).
Structural studies on bioactive compounds. 30. Crystal structure and molecular modeling studies on the Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase cofactor complex with TAB, a highly selective antifolate.
Biochemistry,
39,
3556-3564.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Jan-04
|
Release date:
|
20-Jan-04
|
|
|
Supersedes:
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P16184
(DYR_PNECA) -
Dihydrofolate reductase from Pneumocystis carinii
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
206 a.a.
205 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.1.3
- dihydrofolate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP+ = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
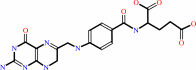 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:3556-3564
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural studies on bioactive compounds. 30. Crystal structure and molecular modeling studies on the Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase cofactor complex with TAB, a highly selective antifolate.
|
|
V.Cody,
D.Chan,
N.Galitsky,
D.Rak,
J.R.Luft,
W.Pangborn,
S.F.Queener,
C.A.Laughton,
M.F.Stevens.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of the ternary complex of NADPH, the potent antifolate [2,
4-diamino-5-¿3-[3-(2-acetyloxyethyl)-3-benzyltriazen-1-yl]-4 -chloroph
enyl¿-6-ethylpyrimidine] (TAB, 1) and Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate
reductase (pcDHFR), refined to 2.1 A resolution, reveals that TAB binds similar
to the antifolates trimethoprim and methotrexate. These data also reveal
multiple conformations for the binding geometry of TAB with two preferred
orientations of the acetyloxy and benzyl groups that results from a 180 degrees
rotation about the N2-N3 triazenyl bond. The methyl of the acetyloxy and benzyl
ring of TAB probes large hydrophobic regions of the p-aminobenzoyl folate
binding pocket of the active site, in particular the region near Phe69, which is
unique to the pcDHFR sequence. These results confirm prior molecular modeling
investigations of the binding of TAB to pcDHFR that identified four low-energy
binding geometries, two involving rotations about the terminal N(2)-N(3)
triazenyl linkage and two involving atropisomerism about the pivotal
pyrimethamine-phenyl bond. The primary differences in the molecular dynamics
(MD) models and those observed in this crystal complex result from small
conformational changes in active-site residues on energy minimization. However,
two MD models place the acetyloxy and benzyl ring groups in a region of the
active site between the cofactor-binding region and the p-aminobenzoyl folate
pocket; an orientation never observed in any DHFR crystal structure to date.
These conformers interact with solvent near the enzyme surface and are probably
not observed due to the loss of specific hydrogen bonds with the enzyme. The
high species pcDHFR selectivity of TAB could be the result of ligand flexibility
that enables multiple binding orientations at the enzyme active site. Further
modification of the acetyloxy region of TAB could increase its potency and
selectivity for pcDHFR.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.R.Bourne,
R.A.Bunce,
P.C.Bourne,
K.D.Berlin,
E.W.Barrow,
and
W.W.Barrow
(2009).
Crystal structure of Bacillus anthracis dihydrofolate reductase with the dihydrophthalazine-based trimethoprim derivative RAB1 provides a structural explanation of potency and selectivity.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
53,
3065-3073.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Balaz
(2009).
Modeling kinetics of subcellular disposition of chemicals.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
109,
1793-1899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Cody,
J.Pace,
K.Chisum,
and
A.Rosowsky
(2006).
New insights into DHFR interactions: analysis of Pneumocystis carinii and mouse DHFR complexes with NADPH and two highly potent 5-(omega-carboxy(alkyloxy) trimethoprim derivatives reveals conformational correlations with activity and novel parallel ring stacking interactions.
|
| |
Proteins,
65,
959-969.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Cody,
J.R.Luft,
W.Pangborn,
and
A.Gangjee
(2003).
Analysis of three crystal structure determinations of a 5-methyl-6-N-methylanilino pyridopyrimidine antifolate complex with human dihydrofolate reductase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1603-1609.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Cody,
N.Galitsky,
J.R.Luft,
W.Pangborn,
and
A.Gangjee
(2003).
Analysis of two polymorphic forms of a pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine N9-C10 reversed-bridge antifolate binary complex with human dihydrofolate reductase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
654-661.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Shrimpton,
and
R.K.Allemann
(2002).
Role of water in the catalytic cycle of E. coli dihydrofolate reductase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1442-1451.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Cody,
N.Galitsky,
J.R.Luft,
W.Pangborn,
A.Rosowsky,
and
S.F.Queener
(2002).
Structure-based enzyme inhibitor design: modeling studies and crystal structure analysis of Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase ternary complex with PT653 and NADPH.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
946-954.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Wang,
J.A.Bruenn,
S.F.Queener,
and
V.Cody
(2001).
Isolation of rat dihydrofolate reductase gene and characterization of recombinant enzyme.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
2517-2523.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

