 |
PDBsum entry 1umh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis of sugar-recognizing ubiquitin ligase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
F-box only protein 2. Chain: a. Fragment: sbd domain. Synonym: fbs1. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. House mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: mouse. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.155
|
R-free:
|
0.192
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Mizushima,T.Hirao,Y.Yoshida,S.J.Lee,T.Chiba,K.Iwai,Y.Yamaguchi, K.Kato,T.Tsukihara,K.Tanaka,Riken Structural Genomics/proteomics Initiative (Rsgi)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
T.Mizushima
et al.
(2004).
Structural basis of sugar-recognizing ubiquitin ligase.
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
365-370.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Oct-03
|
Release date:
|
06-Apr-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q80UW2
(FBX2_MOUSE) -
F-box only protein 2 from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
297 a.a.
184 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.2.19
- Transferred entry: 2.3.2.23, 2.3.2.27 and 6.2.1.45.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + ubiquitin + protein lysine = AMP + diphosphate + protein N-ubiquityllysine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
ubiquitin
|
+
|
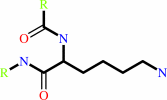 protein lysine
protein lysine
|
=
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
protein N-ubiquityllysine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Mol Biol
11:365-370
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of sugar-recognizing ubiquitin ligase.
|
|
T.Mizushima,
T.Hirao,
Y.Yoshida,
S.J.Lee,
T.Chiba,
K.Iwai,
Y.Yamaguchi,
K.Kato,
T.Tsukihara,
K.Tanaka.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
SCF(Fbs1) is a ubiquitin ligase that functions in the endoplasmic reticulum
(ER)-associated degradation pathway. Fbs1/Fbx2, a member of the F-box proteins,
recognizes high-mannose oligosaccharides. Efficient binding to an N-glycan
requires di-N-acetylchitobiose (chitobiose). Here we report the crystal
structures of the sugar-binding domain (SBD) of Fbs1 alone and in complex with
chitobiose. The SBD is composed of a ten-stranded antiparallel beta-sandwich.
The structure of the SBD-chitobiose complex includes hydrogen bonds between Fbs1
and chitobiose and insertion of the methyl group of chitobiose into a small
hydrophobic pocket of Fbs1. Moreover, NMR spectroscopy has demonstrated that the
amino acid residues adjoining the chitobiose-binding site interact with the
outer branches of the carbohydrate moiety. Considering that the innermost
chitobiose moieties in N-glycans are usually involved in intramolecular
interactions with the polypeptide moieties, we propose that Fbs1 interacts with
the chitobiose in unfolded N-glycoprotein, pointing the protein moiety toward E2
for ubiquitination.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Tertiary structure of SBD in Fbs1. (a) Overall
structure of SBD of Fbs1 shown as a ribbon diagram.  -strands
belonging to S1 and S2 are blue and red, respectively. Loops and
helices are black and yellow, respectively. (b) A topology
diagram of SBD. The -strands
belonging to S1 and S2 are blue and red, respectively. Loops and
helices are black and yellow, respectively. (b) A topology
diagram of SBD. The  -helices
are yellow cylinders labeled -helices
are yellow cylinders labeled  1
and 1
and  2.
The 2.
The  -strands
are arrows labeled -strands
are arrows labeled  1
- 1
-  10.
The left and right forms of 10.
The left and right forms of  -strands
correspond to S1 and S2, respectively, as in a. N and C, N and C
termini, respectively. (c) Amino acid sequences of SBD in Fbs1
and corresponding region of Fbs2. Amino acid residues are
numbered in the N-to-C direction, for example, from position 117
to position 297 (C-terminal end) of Fbs1, and from 69 to 295
(C-terminal end) of Fbs2. Identical residues are boxed.
Secondary structure elements are colored as a. Substrate-binding
residues are red characters. -strands
correspond to S1 and S2, respectively, as in a. N and C, N and C
termini, respectively. (c) Amino acid sequences of SBD in Fbs1
and corresponding region of Fbs2. Amino acid residues are
numbered in the N-to-C direction, for example, from position 117
to position 297 (C-terminal end) of Fbs1, and from 69 to 295
(C-terminal end) of Fbs2. Identical residues are boxed.
Secondary structure elements are colored as a. Substrate-binding
residues are red characters.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Structure of SBD in complex with chitobiose. (a)
Stereo view of the difference-density map (F[o] - F[c] with
phase from the Fbs1 model) of binding chitobiose, contoured at
2.1  ,
modeled into the electron density. ,
modeled into the electron density.  -strands
belonging to S1 and S2 are blue and red, respectively. Loops are
black. The bound chitobiose is orange, and the residues involved
in the substrate binding (FYWK, see Fig. 1c) are green. (b)
Molecular surface representation of the chitobiose-binding
region. The bound chitobiose is shown in ball-and-stick
representation. Two GlcNAc residues are represented by A and B.
Cyan spheres are two water molecules of wild type SBD that are
fixed on the molecular surface through hydrogen bonds with the
backbone N and O of Lys281, respectively. These water molecules
are replaced by O3 and O6 of the chitobiose upon formation of
the SBD -chitobiose complex. (c) Stick representation of the
amino acids involved in binding. Hydrogen bonds are dashed
lines. Oxygen and nitrogen are red and blue, respectively.
Symbols of two water molecules are as in b. -strands
belonging to S1 and S2 are blue and red, respectively. Loops are
black. The bound chitobiose is orange, and the residues involved
in the substrate binding (FYWK, see Fig. 1c) are green. (b)
Molecular surface representation of the chitobiose-binding
region. The bound chitobiose is shown in ball-and-stick
representation. Two GlcNAc residues are represented by A and B.
Cyan spheres are two water molecules of wild type SBD that are
fixed on the molecular surface through hydrogen bonds with the
backbone N and O of Lys281, respectively. These water molecules
are replaced by O3 and O6 of the chitobiose upon formation of
the SBD -chitobiose complex. (c) Stick representation of the
amino acids involved in binding. Hydrogen bonds are dashed
lines. Oxygen and nitrogen are red and blue, respectively.
Symbols of two water molecules are as in b.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Struct Mol Biol
(2004,
11,
365-370)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Sarikas,
T.Hartmann,
and
Z.Q.Pan
(2011).
The cullin protein family.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
12,
220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.M.Duda,
D.C.Scott,
M.F.Calabrese,
E.S.Zimmerman,
N.Zheng,
and
B.A.Schulman
(2011).
Structural regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complexes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
21,
257-264.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gong,
F.Chen,
Y.Pan,
I.Arrieta-Cruz,
Y.Yoshida,
V.Haroutunian,
and
G.M.Pasinetti
(2010).
SCFFbx2-E3-ligase-mediated degradation of BACE1 attenuates Alzheimer's disease amyloidosis and improves synaptic function.
|
| |
Aging Cell,
9,
1018-1031.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Schallus,
K.Fehér,
U.Sternberg,
V.Rybin,
and
C.Muhle-Goll
(2010).
Analysis of the specific interactions between the lectin domain of malectin and diglucosides.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
20,
1010-1020.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Bae,
S.Ohene-Adjei,
S.Kocherginskaya,
R.I.Mackie,
M.A.Spies,
I.K.Cann,
and
S.K.Nair
(2008).
Molecular basis for the selectivity and specificity of ligand recognition by the family 16 carbohydrate-binding modules from Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum ManA.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
12415-12425.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Glenn,
R.F.Nelson,
H.M.Wen,
A.J.Mallinger,
and
H.L.Paulson
(2008).
Diversity in tissue expression, substrate binding, and SCF complex formation for a lectin family of ubiquitin ligases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
12717-12729.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ravid,
and
M.Hochstrasser
(2008).
Diversity of degradation signals in the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
9,
679-690.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Schallus,
C.Jaeckh,
K.Fehér,
A.S.Palma,
Y.Liu,
J.C.Simpson,
M.Mackeen,
G.Stier,
T.J.Gibson,
T.Feizi,
T.Pieler,
and
C.Muhle-Goll
(2008).
Malectin: a novel carbohydrate-binding protein of the endoplasmic reticulum and a candidate player in the early steps of protein N-glycosylation.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
19,
3404-3414.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.T.Dye,
and
B.A.Schulman
(2007).
Structural mechanisms underlying posttranslational modification by ubiquitin-like proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
36,
131-150.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Mizushima,
Y.Yoshida,
T.Kumanomidou,
Y.Hasegawa,
A.Suzuki,
T.Yamane,
and
K.Tanaka
(2007).
Structural basis for the selection of glycosylated substrates by SCF(Fbs1) ubiquitin ligase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
5777-5781.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoshida,
A.Murakami,
K.Iwai,
and
K.Tanaka
(2007).
A neural-specific F-box protein Fbs1 functions as a chaperone suppressing glycoprotein aggregation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
7137-7144.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoshida
(2007).
F-box proteins that contain sugar-binding domains.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
71,
2623-2631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.F.Nelson,
K.A.Glenn,
V.M.Miller,
H.Wen,
and
H.L.Paulson
(2006).
A novel route for F-box protein-mediated ubiquitination links CHIP to glycoprotein quality control.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
20242-20251.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
G.Zhao,
J.J.Truglio,
L.Wang,
G.Li,
W.J.Lennarz,
and
H.Schindelin
(2006).
Structural and biochemical studies of the C-terminal domain of mouse peptide-N-glycanase identify it as a mannose-binding module.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
17214-17219.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ito,
S.Hagihara,
I.Matsuo,
and
K.Totani
(2005).
Structural approaches to the study of oligosaccharides in glycoprotein quality control.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
15,
481-489.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kamiya,
Y.Yamaguchi,
N.Takahashi,
Y.Arata,
K.Kasai,
Y.Ihara,
I.Matsuo,
Y.Ito,
K.Yamamoto,
and
K.Kato
(2005).
Sugar-binding properties of VIP36, an intracellular animal lectin operating as a cargo receptor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
37178-37182.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoshida,
E.Adachi,
K.Fukiya,
K.Iwai,
and
K.Tanaka
(2005).
Glycoprotein-specific ubiquitin ligases recognize N-glycans in unfolded substrates.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
6,
239-244.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Cardozo,
and
M.Pagano
(2004).
The SCF ubiquitin ligase: insights into a molecular machine.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
5,
739-751.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

