 |
PDBsum entry 1n2k

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.6.8
- cerebroside-sulfatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an N-acyl-1-beta-D-(3-O-sulfo)-galactosyl-sphing-4-enine + H2O = a beta- D-galactosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine + sulfate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-acyl-1-beta-D-(3-O-sulfo)-galactosyl-sphing-4-enine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
beta- D-galactosyl-(1<->1')-N-acylsphing-4-enine
|
+
|
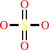 sulfate
sulfate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Inorg Biochem
96:386-392
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of a covalent intermediate of endogenous human arylsulfatase A.
|
|
M.Chruszcz,
P.Laidler,
M.Monkiewicz,
E.Ortlund,
L.Lebioda,
K.Lewinski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structures of human arylsulfatase A crystals soaked in solutions containing
4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate and O-phospho-DL-tyrosine have been determined at
2.7- and 3.2-A resolution, respectively. The formylglycine in position 69, a
residue crucial for catalytic activity, was unambiguously identified in both
structures as forming a covalent bond to the phosphate moiety. A hydroxyl group
is present at the Cbeta of residue 69 and the formation of one out of two
possible stereomeric forms is strongly favoured. The structures confirm the
importance of the gem-diol intermediate in the arylsulfatase's catalytic
mechanism. The presence of an apparently stable covalent bond is consistent with
the weak phosphatase activity observed for human arylsulfatase A. The structures
of the complexes suggest that phosphate ions and phosphate esters inhibit
arylsulfatase in non-covalent and covalent modes, respectively. The metal ion
present in the active site of arylsulfatase A isolated from human placenta is
Ca(2+) and not Mg(2+) as was found in the structure of the recombinant enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kashman,
A.Bishara,
and
M.Aknin
(2010).
Recent N-atom containing compounds from indo-pacific invertebrates.
|
| |
Mar Drugs,
8,
2810-2836.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Schenk,
C.A.Koppisetty,
D.C.Santos,
E.Carmona,
S.Bhatia,
P.G.Nyholm,
and
N.Tanphaichitr
(2009).
Interaction of arylsulfatase-A (ASA) with its natural sulfoglycolipid substrates: a computational and site-directed mutagenesis study.
|
| |
Glycoconj J,
26,
1029-1045.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Kang,
and
R.C.Stevens
(2009).
Structural aspects of therapeutic enzymes to treat metabolic disorders.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
30,
1591-1610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Frese,
S.Schulz,
and
T.Dierks
(2008).
Arylsulfatase G, a novel lysosomal sulfatase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
11388-11395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Felts,
T.J.Reilly,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2006).
Structure of Francisella tularensis AcpA: prototype of a unique superfamily of acid phosphatases and phospholipases C.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
30289-30298.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lingwood,
M.Mylvaganam,
F.Minhas,
B.Binnington,
D.R.Branch,
and
R.Pomès
(2005).
The sulfogalactose moiety of sulfoglycosphingolipids serves as a mimic of tyrosine phosphate in many recognition processes. Prediction and demonstration of Src homology 2 domain/sulfogalactose binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
12542-12547.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Hanson,
M.D.Best,
and
C.H.Wong
(2004).
Sulfatases: structure, mechanism, biological activity, inhibition, and synthetic utility.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
43,
5736-5763.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

