
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase from escherichia coli
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Chain: b, e, h, k. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Chain: c, f, i, l. Ec: 6.3.5.5
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Organism_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,H.M.Holden,G.Wesenberg,F.M.Raushel,I.Rayment
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.B.Thoden
et al.
(1999).
The structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase determined to 2.1 A resolution.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
8.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Mar-97
|
Release date:
|
17-Jun-98
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains B, E, H, K:
E.C.6.3.4.16
- carbamoyl-phosphate synthase (ammonia).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + NH4+ + 2 ATP = carbamoyl phosphate + 2 ADP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 2
×
ATP
2
×
ATP
|
=
|
carbamoyl phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 2
×
ADP
2
×
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains B, C, E, F, H, I, K, L:
E.C.6.3.5.5
- carbamoyl-phosphate synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + L-glutamine + 2 ATP + H2O = carbamoyl phosphate + L-glutamate + 2 ADP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
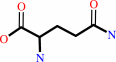 L-glutamine
L-glutamine
|
+
|
 2
×
ATP
2
×
ATP
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
2
×
carbamoyl phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
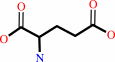 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 2
×
ADP
2
×
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
55:8
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase determined to 2.1 A resolution.
|
|
J.B.Thoden,
F.M.Raushel,
M.M.Benning,
I.Rayment,
H.M.Holden.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the formation of carbamoyl phosphate
from one molecule of bicarbonate, two molecules of Mg2+ATP and one molecule of
glutamine or ammonia depending upon the particular form of the enzyme under
investigation. As isolated from Escherichia coli, the enzyme is an
alpha,beta-heterodimer consisting of a small subunit that hydrolyzes glutamine
and a large subunit that catalyzes the two required phosphorylation events. Here
the three-dimensional structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase from E. coli
refined to 2.1 A resolution with an R factor of 17.9% is described. The small
subunit is distinctly bilobal with a catalytic triad (Cys269, His353 and Glu355)
situated between the two structural domains. As observed in those enzymes
belonging to the alpha/beta-hydrolase family, the active-site nucleophile,
Cys269, is perched at the top of a tight turn. The large subunit consists of
four structural units: the carboxyphosphate synthetic component, the
oligomerization domain, the carbamoyl phosphate synthetic component and the
allosteric domain. Both the carboxyphosphate and carbamoyl phosphate synthetic
components bind Mn2+ADP. In the carboxyphosphate synthetic component, the two
observed Mn2+ ions are both octahedrally coordinated by oxygen-containing
ligands and are bridged by the carboxylate side chain of Glu299. Glu215 plays a
key allosteric role by coordinating to the physiologically important potassium
ion and hydrogen bonding to the ribose hydroxyl groups of ADP. In the carbamoyl
phosphate synthetic component, the single observed Mn2+ ion is also octahedrally
coordinated by oxygen-containing ligands and Glu761 plays a similar role to that
of Glu215. The carboxyphosphate and carbamoyl phosphate synthetic components,
while topologically equivalent, are structurally different, as would be expected
in light of their separate biochemical functions.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7 The active site for the carboxyphosphate synthetic
component. A cartoon of potential hydrogen-bonding interactions
between the ADP/P[i] moiety and the protein is displayed. The
manganese ions are indicated as brown spheres.
|
 |
Figure 13.
Figure 13 A close-up view of the ornithine binding pocket.
Ordered water molecules are indicated by the red spheres. The
carboxylate group of ornithine interacts with the allosteric
domain while the  -amino
group of the side chain forms hydrogen bonds with amino-acid
residues from the carbamoyl phosphate synthetic component. -amino
group of the side chain forms hydrogen bonds with amino-acid
residues from the carbamoyl phosphate synthetic component.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(1999,
55,
8-0)
copyright 1999.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
 Google scholar
Google scholar
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Mollá-Morales,
R.Sarmiento-Mañús,
P.Robles,
V.Quesada,
J.M.Pérez-Pérez,
R.González-Bayón,
M.A.Hannah,
L.Willmitzer,
M.R.Ponce,
and
J.L.Micol
(2011).
Analysis of ven3 and ven6 reticulate mutants reveals the importance of arginine biosynthesis in Arabidopsis leaf development.
|
| |
Plant J,
65,
335-345.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Hart,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2009).
Role of cys-1327 and cys-1337 in redox sensitivity and allosteric monitoring in human carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
5977-5985.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Fan,
L.Lund,
Q.Shao,
Y.Q.Gao,
and
F.M.Raushel
(2009).
A combined theoretical and experimental study of the ammonia tunnel in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
10211-10219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
H.M.Holden,
and
S.M.Firestine
(2008).
Structural analysis of the active site geometry of N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
13346-13353.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kuriyan,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2007).
The origin of protein interactions and allostery in colocalization.
|
| |
Nature,
450,
983-990.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Conformational changes in ammonia-channeling glutamine amidotransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
17,
653-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Abbott,
J.M.Newell,
C.M.Lightcap,
M.E.Olanich,
D.T.Loughlin,
M.A.Weller,
G.Lam,
S.Pollack,
and
W.A.Patton
(2006).
The effects of removing the GAT domain from E. coli GMP synthetase.
|
| |
Protein J,
25,
483-491.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Schmitt,
M.Panvert,
S.Blanquet,
and
Y.Mechulam
(2005).
Structural basis for tRNA-dependent amidotransferase function.
|
| |
Structure,
13,
1421-1433.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kothe,
C.Purcarea,
H.I.Guy,
D.R.Evans,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2005).
Direct demonstration of carbamoyl phosphate formation on the C-terminal domain of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
37-44.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kothe,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2004).
Nucleotide recognition in the ATP-grasp protein carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
466-475.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Serre,
B.Penverne,
J.L.Souciet,
S.Potier,
H.Guy,
D.Evans,
P.Vicart,
and
G.Hervé
(2004).
Integrated allosteric regulation in the S. cerevisiae carbamylphosphate synthetase - aspartate transcarbamylase multifunctional protein.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
5,
6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Johnston,
V.L.Arcus,
C.J.Morton,
M.W.Parker,
and
E.N.Baker
(2003).
Crystal structure of a putative methyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: misannotation of a genome clarified by protein structural analysis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
185,
4057-4065.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Saeed-Kothe,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2002).
Specificity determining residues in ammonia- and glutamine-dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthetases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
7231-7238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Eroglu,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2002).
Unmasking a functional allosteric domain in an allosterically nonresponsive carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
45466-45472.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Li,
T.J.Ryan,
K.J.Chave,
and
P.Van Roey
(2002).
Three-dimensional structure of human gamma -glutamyl hydrolase. A class I glatamine amidotransferase adapted for a complex substate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
24522-24529.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
X.Huang,
F.M.Raushel,
and
H.M.Holden
(2002).
Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase. Creation of an escape route for ammonia.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
39722-39727.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Dengler,
A.S.Siddiqui,
and
G.J.Barton
(2001).
Protein structural domains: analysis of the 3Dee domains database.
|
| |
Proteins,
42,
332-344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Snel,
P.Bork,
and
M.Huynen
(2000).
Genome evolution. Gene fusion versus gene fission.
|
| |
Trends Genet,
16,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Javid-Majd,
L.S.Mullins,
F.M.Raushel,
and
M.A.Stapleton
(2000).
The differentially conserved residues of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
5073-5080.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
C.Z.Blanchard,
H.M.Holden,
and
G.L.Waldrop
(2000).
Movement of the biotin carboxylase B-domain as a result of ATP binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
16183-16190.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Y.Galperin,
and
N.V.Grishin
(2000).
The synthetase domains of cobalamin biosynthesis amidotransferases cobB and cobQ belong to a new family of ATP-dependent amidoligases, related to dethiobiotin synthetase.
|
| |
Proteins,
41,
238-247.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Hewagama,
H.I.Guy,
J.F.Vickrey,
and
D.R.Evans
(1999).
Functional linkage between the glutaminase and synthetase domains of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase. Role of serine 44 in carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase-aspartate carbamoyltransferase-dihydroorotase (cad).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
28240-28245.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.W.Miles,
S.Rhee,
and
D.R.Davies
(1999).
The molecular basis of substrate channeling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
12193-12196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
F.M.Raushel,
G.Wesenberg,
and
H.M.Holden
(1999).
The binding of inosine monophosphate to Escherichia coli carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
22502-22507.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

