
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
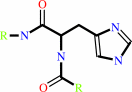
Chain F:
E.C.2.7.1.69
- Transferred entry: 2.7.1.191, 2.7.1.192, 2.7.1.193, 2.7.1.194, 2.7.1.195,
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
+
|
|
=
|
|
+
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain G:
E.C.2.7.1.30
- glycerol kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
glycerol + ATP = sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
sn-glycerol 3-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
91:3544-3548
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cation-promoted association of a regulatory and target protein is controlled by protein phosphorylation.
|
|
M.Feese,
D.W.Pettigrew,
N.D.Meadow,
S.Roseman,
S.J.Remington.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A central question in molecular biology concerns the means by which a regulatory
protein recognizes different targets. IIIGlc, the glucose-specific
phosphocarrier protein of the bacterial phosphotransferase system, is also the
central regulatory element of the PTS. Binding of unphosphorylated IIIGlc
inhibits several non-PTS proteins, but there is little or no sequence similarity
between IIIGlc binding sites on different target proteins. The crystal structure
of Escherichia coli IIIGlc bound to one of its regulatory targets, glycerol
kinase, has been refined at 2.6-A resolution in the presence of products,
adenosine diphosphate and glycerol 3-phosphate. Structural and kinetic analyses
show that the complex of IIIGlc with glycerol kinase creates an intermolecular
Zn(II) binding site with ligation identical to that of the zinc peptidase
thermolysin. The zinc is coordinated by the two active-site histidines of
IIIGlc, a glutamate of glycerol kinase, and a water molecule. Zn(II) at 0.01 and
0.1 mM decreases the Ki of IIIGlc for glycerol kinase by factors of about 15 and
60, respectively. The phosphorylation of one of the histidines of IIIGlc, in its
alternative role as phosphocarrier, provides an elegant means of controlling the
cation-enhanced protein-protein regulatory interaction. The need for the target
protein to supply only one metal ligand may account for the lack of sequence
similarity among the regulatory targets of IIIGlc.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Pettigrew
(2009).
Amino acid substitutions in the sugar kinase/hsp70/actin superfamily conserved ATPase core of E. coli glycerol kinase modulate allosteric ligand affinity but do not alter allosteric coupling.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
481,
151-156.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Pettigrew
(2009).
Oligomeric interactions provide alternatives to direct steric modes of control of sugar kinase/actin/hsp70 superfamily functions by heterotropic allosteric effectors: inhibition of E. coli glycerol kinase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
492,
29-39.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Diao,
and
M.S.Hasson
(2009).
Crystal structure of butyrate kinase 2 from Thermotoga maritima, a member of the ASKHA superfamily of phosphotransferases.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
2521-2529.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Katsumi,
Y.Koga,
D.J.You,
H.Matsumura,
K.Takano,
and
S.Kanaya
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction study of glycerol kinase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
126-129.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Deutscher,
C.Francke,
and
P.W.Postma
(2006).
How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
70,
939.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Grayson,
E.Tajkhorshid,
and
K.Schulten
(2003).
Mechanisms of selectivity in channels and enzymes studied with interactive molecular dynamics.
|
| |
Biophys J,
85,
36-48.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Pawlyk,
and
D.W.Pettigrew
(2002).
Transplanting allosteric control of enzyme activity by protein-protein interactions: coupling a regulatory site to the conserved catalytic core.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
11115-11120.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Huang,
T.Inoue,
K.Ito,
and
T.Yoshimoto
(2001).
Preliminary crystallographic study of Thermus aquaticus glycerol kinase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
1030-1031.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Gorokhov,
L.Perera,
T.A.Darden,
M.Negishi,
L.C.Pedersen,
and
L.G.Pedersen
(2000).
Heparan sulfate biosynthesis: a theoretical study of the initial sulfation step by N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase.
|
| |
Biophys J,
79,
2909-2917.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.G.Hymowitz,
M.P.O'Connell,
M.H.Ultsch,
A.Hurst,
K.Totpal,
A.Ashkenazi,
A.M.de Vos,
and
R.F.Kelley
(2000).
A unique zinc-binding site revealed by a high-resolution X-ray structure of homotrimeric Apo2L/TRAIL.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
633-640.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.T.Robillard,
and
J.Broos
(1999).
Structure/function studies on the bacterial carbohydrate transporters, enzymes II, of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1422,
73.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Gunnewijk,
P.W.Postma,
and
B.Poolman
(1999).
Phosphorylation and functional properties of the IIA domain of the lactose transport protein of Streptococcus thermophilus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
181,
632-641.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Pettigrew,
N.D.Meadow,
S.Roseman,
and
S.J.Remington
(1998).
Cation-promoted association of Escherichia coli phosphocarrier protein IIAGlc with regulatory target protein glycerol kinase: substitutions of a Zinc(II) ligand and implications for inducer exclusion.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
4875-4883.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Feese,
H.R.Faber,
C.E.Bystrom,
D.W.Pettigrew,
and
S.J.Remington
(1998).
Glycerol kinase from Escherichia coli and an Ala65-->Thr mutant: the crystal structures reveal conformational changes with implications for allosteric regulation.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
1407-1418.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kato,
T.Mizuno,
T.Shimizu,
and
T.Hakoshima
(1997).
Insights into multistep phosphorelay from the crystal structure of the C-terminal HPt domain of ArcB.
|
| |
Cell,
88,
717-723.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.McEvoy,
and
F.W.Dahlquist
(1997).
Phosphohistidines in bacterial signaling.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
793-797.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.P.Zhu,
N.Nosworthy,
A.Ginsburg,
M.Miyata,
Y.J.Seok,
and
A.Peterkofsky
(1997).
Expression, purification, and characterization of enzyme IIA(glc) of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Mycoplasma capricolum.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
6947-6953.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Gerloff,
and
F.E.Cohen
(1996).
Secondary structure prediction and unrefined tertiary structure prediction for cyclin A, B, and D.
|
| |
Proteins,
24,
18-34.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Pettigrew,
W.Z.Liu,
C.Holmes,
N.D.Meadow,
and
S.Roseman
(1996).
A single amino acid change in Escherichia coli glycerol kinase abolishes glucose control of glycerol utilization in vivo.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
178,
2846-2852.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

