 |
PDBsum entry 1g6c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Thiamin phosphate synthase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Thiamin phosphate synthase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Other_details: complexed with 2-trifluoromethyl-5-methylene-5h- pyrimidin-4-ylideneamine, 4-methyl-5-hydroxyethylthiazole phosphate and pyrophosphate
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus subtilis. Organism_taxid: 1423. Gene: thic. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.215
|
R-free:
|
0.237
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.H.Peapus,H.-J.Chiu,N.Campobasso,J.J.Reddick,T.P.Begley,S.E.Ealick
|
Key ref:

|
 |
D.H.Peapus
et al.
(2001).
Structural characterization of the enzyme-substrate, enzyme-intermediate, and enzyme-product complexes of thiamin phosphate synthase.
Biochemistry,
40,
10103-10114.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Nov-00
|
Release date:
|
26-Sep-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P39594
(THIE_BACSU) -
Thiamine-phosphate synthase from Bacillus subtilis (strain 168)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
222 a.a.
226 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.3
- thiamine phosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
2-[(2R,5Z)-2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5(2H)-ylidene]ethyl phosphate + 4-amino-2-methyl-5-(diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine + 2 H+ = thiamine phosphate + CO2 + diphosphate
|
|
2.
|
2-(2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl phosphate + 4-amino-2-methyl- 5-(diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine + 2 H+ = thiamine phosphate + CO2 + diphosphate
|
|
3.
|
4-methyl-5-(2-phosphooxyethyl)-thiazole + 4-amino-2-methyl-5- (diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine + H+ = thiamine phosphate + diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-[(2R,5Z)-2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5(2H)-ylidene]ethyl phosphate
|
+
|
4-amino-2-methyl-5-(diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
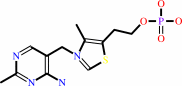 thiamine phosphate
thiamine phosphate
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.09% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-(2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl phosphate
|
+
|
4-amino-2-methyl- 5-(diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
 thiamine phosphate
thiamine phosphate
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.09% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-methyl-5-(2-phosphooxyethyl)-thiazole
|
+
|
4-amino-2-methyl-5- (diphosphooxymethyl)pyrimidine
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
thiamine phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.09% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
40:10103-10114
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural characterization of the enzyme-substrate, enzyme-intermediate, and enzyme-product complexes of thiamin phosphate synthase.
|
|
D.H.Peapus,
H.J.Chiu,
N.Campobasso,
J.J.Reddick,
T.P.Begley,
S.E.Ealick.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thiamin phosphate synthase catalyzes the formation of thiamin phosphate from
4-amino-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyrimidine pyrophosphate and
5-(hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazole phosphate. Several lines of evidence suggest
that the reaction proceeds via a dissociative mechanism. The previously
determined crystal structure of thiamin phosphate synthase in complex with the
reaction products, thiamin phosphate and magnesium pyrophosphate, provided a
view of the active site and suggested a number of additional experiments. We
report here seven new crystal structures primarily involving crystals of S130A
thiamin phosphate synthase soaked in solutions containing substrates or
products. We prepared S130A thiamin phosphate synthase with the intent of
characterizing the enzyme-substrate complex. Surprisingly, in three thiamin
phosphate synthase structures, the active site density cannot be modeled as
either substrates or products. For these structures, the best fit to the
electron density is provided by a model that consists of independent pyrimidine,
pyrophosphate, and thiazole phosphate fragments, consistent with a carbenium ion
intermediate. The resulting carbenium ion is likely to be further stabilized by
proton transfer from the pyrimidine amino group to the pyrophosphate to give the
pyrimidine iminemethide, which we believe is the species that is observed in the
crystal structures.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Paul,
S.E.O'Leary,
K.Rajashankar,
W.Bu,
A.Toms,
E.C.Settembre,
J.M.Sanders,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2010).
Glycal formation in crystals of uridine phosphorylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
3499-3509.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Borisova,
B.T.Circello,
J.K.Zhang,
W.A.van der Donk,
and
W.W.Metcalf
(2010).
Biosynthesis of rhizocticins, antifungal phosphonate oligopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis ATCC6633.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
28-37.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Jurgenson,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2009).
The structural and biochemical foundations of thiamin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
78,
569-603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Hanes,
S.E.Ealick,
and
T.P.Begley
(2007).
Thiamin phosphate synthase: the rate of pyrimidine carbocation formation.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
4860-4861.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lehmann,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2006).
Structure of the Escherichia coli ThiS-ThiF complex, a key component of the sulfur transfer system in thiamin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
11-19.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Wrenger,
M.L.Eschbach,
I.B.Müller,
N.P.Laun,
T.P.Begley,
and
R.D.Walter
(2006).
Vitamin B1 de novo synthesis in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum depends on external provision of 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
387,
41-51.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Yang,
and
C.H.Tung
(2006).
Protein structure database search and evolutionary classification.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
34,
3646-3659.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.V.Murphy,
and
P.J.Rutledge
(2006).
Symbiosis in chemistry and biology.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
2,
59-62.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.S.Chappie,
J.M.Cànaves,
G.W.Han,
C.L.Rife,
Q.Xu,
and
R.C.Stevens
(2005).
The structure of a eukaryotic nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase reveals structural heterogeneity among type II PRTases.
|
| |
Structure,
13,
1385-1396.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Cheek,
Y.Qi,
S.S.Krishna,
L.N.Kinch,
and
N.V.Grishin
(2004).
4SCOPmap: automated assignment of protein structures to evolutionary superfamilies.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
5,
197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Settembre,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2003).
Structural biology of enzymes of the thiamin biosynthesis pathway.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
13,
739-747.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

