 |
PDBsum entry 1g0y

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Immune system
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1g0y
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain R:
E.C.3.2.2.6
- ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + H2O = ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
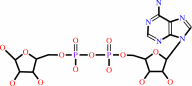 ADP-D-ribose
ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
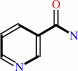 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
275:36927-36933
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
X-ray crystal structure of a small antagonist peptide bound to interleukin-1 receptor type 1.
|
|
G.P.Vigers,
D.J.Dripps,
C.K.Edwards,
B.J.Brandhuber.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Interleukin (IL-1)alpha and IL-1beta are important mediators of inflammation.
The binding of IL-1 to interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) type 1 is the initial step
in IL-1 signal transduction and therefore is a tempting target for
anti-inflammatory therapeutics. To advance our understanding of IL-1R1 binding
interactions, we have determined the structure of the extracellular domains of
IL-1R1 bound to a 21-amino acid IL-1 antagonist peptide at 3.0-A resolution. The
antagonist peptide binds to the domain 1/2 junction of the receptor, which is a
conserved binding site for IL-1beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). This
co-crystal structure also reveals that considerable flexibility is present in
IL-1R1 because the carboxyl-terminal domain of the receptor is rotated almost
170 degrees relative to the first two domains of the receptor compared with the
previously solved IL-1R1.ligand structures. The structure shows an unexpected
binding mode for the peptide and may contribute to the design of smaller IL-1R
antagonists.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Structures of IL-1R1·IL-1  and
IL-1R1·IL-1ra. Shown is a comparison of the structures of
the IL-1R1·IL-1 and
IL-1R1·IL-1ra. Shown is a comparison of the structures of
the IL-1R1·IL-1  complex
(left) and the IL-1R1·IL-1ra complex (right). The two
structures look very similar, but in the IL-1ra complex, the
third domain swings 20° away from the ligand. The receptor
is orientated such that the cell membrane, if present, would be
at the bottom of the figure. The amino terminus of the receptor
is at the top right, and the carboxyl terminus at the bottom.
The conserved binding site (Site A) lies between the first and
second immunoglobulin domains, whereas the second binding site
(Site B), which is utilized by IL-1 complex
(left) and the IL-1R1·IL-1ra complex (right). The two
structures look very similar, but in the IL-1ra complex, the
third domain swings 20° away from the ligand. The receptor
is orientated such that the cell membrane, if present, would be
at the bottom of the figure. The amino terminus of the receptor
is at the top right, and the carboxyl terminus at the bottom.
The conserved binding site (Site A) lies between the first and
second immunoglobulin domains, whereas the second binding site
(Site B), which is utilized by IL-1  , but not by
IL-1ra, lies on the face of the third domain. The structures are
colored by change in solvent-accessible surface upon ligand
binding. The color scheme ranges from dark blue (<20 Å2) to red
(>90 Å2). , but not by
IL-1ra, lies on the face of the third domain. The structures are
colored by change in solvent-accessible surface upon ligand
binding. The color scheme ranges from dark blue (<20 Å2) to red
(>90 Å2).
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Structure of the IL-1R1· AF10847 complex.
Left, the orientation of the first and second domains of IL-1R1
is the same as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The third
domain has swung around 168° to touch the first domain, and
binding Site B now faces away from the ligand. The peptide forms
an  -helix
through Site A, with two long strands lying along the sides of
IL-1R1. IL-1R1 is colored by secondary structure, and AF10847 is
magenta. Right, the same complex is shown, viewed from the "top"
of the receptor, looking into Site A. This view shows how the
tails of the peptide (shown in magenta) wrap around IL-1R1. -helix
through Site A, with two long strands lying along the sides of
IL-1R1. IL-1R1 is colored by secondary structure, and AF10847 is
magenta. Right, the same complex is shown, viewed from the "top"
of the receptor, looking into Site A. This view shows how the
tails of the peptide (shown in magenta) wrap around IL-1R1.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2000,
275,
36927-36933)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Karaca,
and
A.M.Bonvin
(2011).
A multidomain flexible docking approach to deal with large conformational changes in the modeling of biomolecular complexes.
|
| |
Structure,
19,
555-565.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Wang,
S.Zhang,
L.Li,
X.Liu,
K.Mei,
and
X.Wang
(2010).
Structural insights into the assembly and activation of IL-1β with its receptors.
|
| |
Nat Immunol,
11,
905-911.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Lingel,
T.M.Weiss,
M.Niebuhr,
B.Pan,
B.A.Appleton,
C.Wiesmann,
J.F.Bazan,
and
W.J.Fairbrother
(2009).
Structure of IL-33 and its interaction with the ST2 and IL-1RAcP receptors--insight into heterotrimeric IL-1 signaling complexes.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
1398-1410.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Somani,
C.P.Chng,
and
C.S.Verma
(2007).
Hydration of a hydrophobic cavity and its functional role: a simulation study of human interleukin-1beta.
|
| |
Proteins,
67,
868-885.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Langer,
E.C.Cutrone,
and
S.Kotenko
(2004).
The Class II cytokine receptor (CRF2) family: overview and patterns of receptor-ligand interactions.
|
| |
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev,
15,
33-48.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Sims
(2002).
IL-1 and IL-18 receptors, and their extended family.
|
| |
Curr Opin Immunol,
14,
117-122.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Rich,
and
D.G.Myszka
(2001).
Survey of the year 2000 commercial optical biosensor literature.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
14,
273-294.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

