
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
X-ray structure of the haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein of influenza c virus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein. Chain: a, c, e. Fragment: hef1. Engineered: yes. Haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein. Chain: b, d, f. Fragment: hef2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Influenza c virus (c/johannesburg/1/66). Organism_taxid: 100673. Strain: c/johannesburg/1/66. Strain: c/johannesburg/1/66
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Hexamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.223
|
R-free:
|
0.267
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.B.Rosenthal,X.Zhang,F.Formanowski,W.Fitz,C.H.Wong,H.Meier-Ewert, J.J.Skehel,D.C.Wiley
|
Key ref:

|
 |
P.B.Rosenthal
et al.
(1998).
Structure of the haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein of influenza C virus.
Nature,
396,
92-96.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Feb-99
|
Release date:
|
01-Mar-00
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F:
E.C.3.1.1.53
- sialate O-acetylesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate + H2O = N-acetylneuraminate + acetate + H+
|
|
2.
|
N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate + H2O = N-acetylneuraminate + acetate + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate
N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
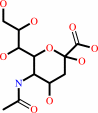 N-acetylneuraminate
N-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
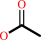 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.09% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
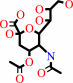 N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate
N-acetyl-4-O-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 N-acetylneuraminate
N-acetylneuraminate
|
+
|
 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.09% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nature
396:92-96
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of the haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein of influenza C virus.
|
|
P.B.Rosenthal,
X.Zhang,
F.Formanowski,
W.Fitz,
C.H.Wong,
H.Meier-Ewert,
J.J.Skehel,
D.C.Wiley.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The spike glycoproteins of the lipid-enveloped orthomyxoviruses and
paramyxoviruses have three functions: to recognize the receptor on the cell
surface, to mediate viral fusion with the cell membrane, and to destroy the
receptor. In influenza C virus, a single glycoprotein, the
haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion (HEF) protein, possesses all three functions. In
influenza A and B, the first two activities are mediated by haemagglutinin and
the third by a second glycoprotein, neuraminidase. Here we report the crystal
structure of the HEF envelope glycoprotein of influenza C virus. We have
identified the receptor-binding site and the receptor-destroying enzyme
(9-O-acetylesterase) sites, by using receptor analogues. The receptor-binding
domain is structurally similar to the sialic acid-binding domain of influenza A
haemagglutinin, but binds 9-O-acetylsialic acid. The esterase domain has a
structure similar to the esterase from Streptomyces scabies and a brain
acetylhydrolase. The receptor domain is inserted into a surface loop of the
esterase domain and the esterase domain is inserted into a surface loop of the
stem. The stem domain is similar to that of influenza A haemagglutinin, except
that the triple-stranded, alpha-helical bundle diverges at both of its ends, and
the amino terminus of HEF2, the fusion peptide, is partially exposed. The
segregation of HEF's three functions into structurally distinct domains suggests
that the entire stem region, including sequences at the amino and carboxy
termini of HEF1 which precede the post-translational cleavage site between HEF1
and HEF2, forms an independent fusion domain which is probably derived from an
ancestral membrane fusion protein.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein
structure. a, The structure of the HEF trimer. HEF1 (blue), HEF2
(red), receptor analogue and enzyme inhibitor ligands, yellow; N
-linked carbohydrate ball-and-stick (purple). HEF1 is linked to
HEF2 by a disulfide bond from Cys 6 of HEF1 to Cys 137 of HEF2.
b, Monomer surface of HEF (Grasp27) showing 9-O -acetylsialoside
receptor binding site (top) and 9-O -acetylesterase site
(bottom). Inset, the esterase removes the acetyl group of 9-O
-acetylsialic acid (see arrow).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 HEF receptor binding. a, Ligand bound to the
receptor-binding site. Potential hydrogen bonds are indicated in
green or red for those conserved in HA ligand binding. Four
polar contacts are formed with the ligand identically in HEF and
HA: two from the hydroxyl group of HEF1 Tyr 127 (Y98 in HA1) to
the 8-hydroxyl and 9-amide of the ligands and two from
main-chain atoms: the carbonyl oxygen of HEF1 residue 170 (135
in HA1) to the 5-amide of the ligand and the amide of HEF1 172
(137 in HA1) to the carboxylate of the ligand. The acetyl methyl
group binds in a nonpolar pocket unique to HEF, formed by Phe
225 and 293, and Pro 271; the acetyl carbonyl oxygen contacts
the hydroxyl group of Tyr 224 and the guanidino group of Arg
236. b, Comparison of architecture of the HEF and HA binding
sites. The figure was constructed by superimposing the common
parts of the ligands in HA and HEF.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nature
(1998,
396,
92-96)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Stanley,
J.Mayr,
W.Huber,
R.Vlasak,
and
H.Streicher
(2011).
Synthesis and inhibitory activity of sialic acid derivatives targeted at viral sialate-O-acetylesterases.
|
| |
Eur J Med Chem,
46,
2852-2860.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Indu,
V.Kochat,
S.Thakurela,
C.Ramakrishnan,
and
R.Varadarajan
(2011).
Conformational analysis and design of cross-strand disulfides in antiparallel β-sheets.
|
| |
Proteins,
79,
244-260.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Gatherer
(2010).
Tempo and mode in the molecular evolution of influenza C.
|
| |
PLoS Curr,
2,
RRN1199.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yang,
L.M.Chen,
P.J.Carney,
R.O.Donis,
and
J.Stevens
(2010).
Structures of receptor complexes of a North American H7N2 influenza hemagglutinin with a loop deletion in the receptor binding site.
|
| |
PLoS Pathog,
6,
e1001081.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Langereis,
A.L.van Vliet,
W.Boot,
and
R.J.de Groot
(2010).
Attachment of mouse hepatitis virus to O-acetylated sialic acid is mediated by hemagglutinin-esterase and not by the spike protein.
|
| |
J Virol,
84,
8970-8974.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Langereis,
Q.Zeng,
G.J.Gerwig,
B.Frey,
M.von Itzstein,
J.P.Kamerling,
R.J.de Groot,
and
E.G.Huizinga
(2009).
Structural basis for ligand and substrate recognition by torovirus hemagglutinin esterases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
15897-15902.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Mesecar,
and
K.Ratia
(2008).
Viral destruction of cell surface receptors.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
8807-8808.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Garry,
and
R.F.Garry
(2008).
Proteomics computational analyses suggest that baculovirus GP64 superfamily proteins are class III penetrenes.
|
| |
Virol J,
5,
28.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Martínez-Martínez,
J.Navarro-Fernández,
J.Daniel Lozada-Ramírez,
F.García-Carmona,
and
A.Sánchez-Ferrer
(2008).
YesT: a new rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
379-388.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Lee,
M.L.Fusco,
A.J.Hessell,
W.B.Oswald,
D.R.Burton,
and
E.O.Saphire
(2008).
Structure of the Ebola virus glycoprotein bound to an antibody from a human survivor.
|
| |
Nature,
454,
177-182.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Mayr,
T.Haselhorst,
M.A.Langereis,
J.C.Dyason,
W.Huber,
B.Frey,
R.Vlasak,
R.J.de Groot,
and
M.von Itzstein
(2008).
Influenza C virus and bovine coronavirus esterase reveal a similar catalytic mechanism: new insights for drug discovery.
|
| |
Glycoconj J,
25,
393-399.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Navarro-Fernández,
I.Martínez-Martínez,
S.Montoro-García,
F.García-Carmona,
H.Takami,
and
A.Sánchez-Ferrer
(2008).
Characterization of a new rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase from Bacillus halodurans C-125 with a new putative carbohydrate binding domain.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
1375-1382.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Song,
V.Nakaar,
U.Kavita,
A.Price,
J.Huleatt,
J.Tang,
A.Jacobs,
G.Liu,
Y.Huang,
P.Desai,
G.Maksymiuk,
V.Takahashi,
S.Umlauf,
L.Reiserova,
R.Bell,
H.Li,
Y.Zhang,
W.F.McDonald,
T.J.Powell,
and
L.Tussey
(2008).
Efficacious recombinant influenza vaccines produced by high yield bacterial expression: a solution to global pandemic and seasonal needs.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e2257.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Gao,
E.W.Brydon,
and
P.Palese
(2008).
A seven-segmented influenza A virus expressing the influenza C virus glycoprotein HEF.
|
| |
J Virol,
82,
6419-6426.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Wang,
F.Cheng,
M.Lu,
X.Tian,
and
J.Ma
(2008).
Crystal structure of unliganded influenza B virus hemagglutinin.
|
| |
J Virol,
82,
3011-3020.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zeng,
M.A.Langereis,
A.L.van Vliet,
E.G.Huizinga,
and
R.J.de Groot
(2008).
Structure of coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase offers insight into corona and influenza virus evolution.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
9065-9069.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Crescenzo-Chaigne,
and
S.van der Werf
(2007).
Rescue of influenza C virus from recombinant DNA.
|
| |
J Virol,
81,
11282-11289.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Zhukovsky,
I.Markovic,
and
A.L.Bailey
(2007).
Influence of calcium on lipid mixing mediated by influenza hemagglutinin.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
465,
101-108.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Frank,
and
R.M.Bush
(2007).
Barriers to antigenic escape by pathogens: trade-off between reproductive rate and antigenic mutability.
|
| |
BMC Evol Biol,
7,
229.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Cingolani,
D.Andrews,
and
S.Casjens
(2006).
Crystallogenesis of bacteriophage P22 tail accessory factor gp26 at acidic and neutral pH.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
477-482.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Russell,
D.J.Stevens,
L.F.Haire,
S.J.Gamblin,
and
J.J.Skehel
(2006).
Avian and human receptor binding by hemagglutinins of influenza A viruses.
|
| |
Glycoconj J,
23,
85-92.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.de Groot
(2006).
Structure, function and evolution of the hemagglutinin-esterase proteins of corona- and toroviruses.
|
| |
Glycoconj J,
23,
59-72.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Bitto,
C.A.Bingman,
J.G.McCoy,
S.T.Allard,
G.E.Wesenberg,
and
G.N.Phillips
(2005).
The structure at 1.6 Angstroms resolution of the protein product of the At4g34215 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1655-1661.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Smits,
G.J.Gerwig,
A.L.van Vliet,
A.Lissenberg,
P.Briza,
J.P.Kamerling,
R.Vlasak,
and
R.J.de Groot
(2005).
Nidovirus sialate-O-acetylesterases: evolution and substrate specificity of coronaviral and toroviral receptor-destroying enzymes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
6933-6941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Hellebø,
U.Vilas,
K.Falk,
and
R.Vlasak
(2004).
Infectious salmon anemia virus specifically binds to and hydrolyzes 4-O-acetylated sialic acids.
|
| |
J Virol,
78,
3055-3062.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Stevens,
A.L.Corper,
C.F.Basler,
J.K.Taubenberger,
P.Palese,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2004).
Structure of the uncleaved human H1 hemagglutinin from the extinct 1918 influenza virus.
|
| |
Science,
303,
1866-1870.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Timmins,
R.W.Ruigrok,
and
W.Weissenhorn
(2004).
Structural studies on the Ebola virus matrix protein VP40 indicate that matrix proteins of enveloped RNA viruses are analogues but not homologues.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
233,
179-186.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Falk,
V.Aspehaug,
R.Vlasak,
and
C.Endresen
(2004).
Identification and characterization of viral structural proteins of infectious salmon anemia virus.
|
| |
J Virol,
78,
3063-3071.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Wouters,
K.K.Lau,
and
P.J.Hogg
(2004).
Cross-strand disulphides in cell entry proteins: poised to act.
|
| |
Bioessays,
26,
73-79.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Barnett,
D.L.Wensel,
W.Li,
D.Fass,
and
J.M.Cunningham
(2003).
Structure and mechanism of a coreceptor for infection by a pathogenic feline retrovirus.
|
| |
J Virol,
77,
2717-2729.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.A.Rey
(2003).
Dengue virus envelope glycoprotein structure: new insight into its interactions during viral entry.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
6899-6901.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Piñón,
S.M.Kelly,
N.C.Price,
J.U.Flanagan,
and
D.W.Brighty
(2003).
An antiviral peptide targets a coiled-coil domain of the human T-cell leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein.
|
| |
J Virol,
77,
3281-3290.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Ludwig,
B.Baljinnyam,
A.Herrmann,
and
C.Böttcher
(2003).
The 3D structure of the fusion primed Sendai F-protein determined by electron cryomicroscopy.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
3761-3771.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Steinhauer,
and
J.J.Skehel
(2002).
Genetics of influenza viruses.
|
| |
Annu Rev Genet,
36,
305-332.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Malisan,
L.Franchi,
B.Tomassini,
N.Ventura,
I.Condò,
M.R.Rippo,
A.Rufini,
L.Liberati,
C.Nachtigall,
B.Kniep,
and
R.Testi
(2002).
Acetylation suppresses the proapoptotic activity of GD3 ganglioside.
|
| |
J Exp Med,
196,
1535-1541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Wagner,
M.Matrosovich,
and
H.D.Klenk
(2002).
Functional balance between haemagglutinin and neuraminidase in influenza virus infections.
|
| |
Rev Med Virol,
12,
159-166.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ha,
D.J.Stevens,
J.J.Skehel,
and
D.C.Wiley
(2002).
H5 avian and H9 swine influenza virus haemagglutinin structures: possible origin of influenza subtypes.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
865-875.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Barnett,
R.A.Davey,
and
J.M.Cunningham
(2001).
Modular organization of the Friend murine leukemia virus envelope protein underlies the mechanism of infection.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
4113-4118.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Allison,
J.Schalich,
K.Stiasny,
C.W.Mandl,
and
F.X.Heinz
(2001).
Mutational evidence for an internal fusion peptide in flavivirus envelope protein E.
|
| |
J Virol,
75,
4268-4275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.V.Pletnev,
W.Zhang,
S.Mukhopadhyay,
B.R.Fisher,
R.Hernandez,
D.T.Brown,
T.S.Baker,
M.G.Rossmann,
and
R.J.Kuhn
(2001).
Locations of carbohydrate sites on alphavirus glycoproteins show that E1 forms an icosahedral scaffold.
|
| |
Cell,
105,
127-136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Maerz,
R.J.Center,
B.E.Kemp,
B.Kobe,
and
P.Poumbourios
(2000).
Functional implications of the human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein helical hairpin structure.
|
| |
J Virol,
74,
6614-6621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Im,
and
M.H.Yu
(2000).
Role of Lys335 in the metastability and function of inhibitory serpins.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
934-941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Braakman,
and
E.van Anken
(2000).
Folding of viral envelope glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum.
|
| |
Traffic,
1,
533-539.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Féthière,
A.Andersson,
K.Keinänen,
and
D.R.Madden
(2000).
Crystallization of an AMPA receptor binding domain without agonist: importance of carbohydrate content and flash-cooling conditions.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
1625-1629.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Skehel,
and
D.C.Wiley
(2000).
Receptor binding and membrane fusion in virus entry: the influenza hemagglutinin.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
69,
531-569.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Matthews,
T.F.Young,
S.P.Tucker,
and
J.P.Mackay
(2000).
The core of the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein is a trimeric coiled coil.
|
| |
J Virol,
74,
5911-5920.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Pekosz,
and
R.A.Lamb
(1999).
Cell surface expression of biologically active influenza C virus HEF glycoprotein expressed from cDNA.
|
| |
J Virol,
73,
8808-8812.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Baker,
R.E.Dutch,
R.A.Lamb,
and
T.S.Jardetzky
(1999).
Structural basis for paramyxovirus-mediated membrane fusion.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
3,
309-319.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Vijayan,
and
N.Chandra
(1999).
Lectins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
9,
707-714.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhang,
P.B.Rosenthal,
F.Formanowski,
W.Fitz,
C.H.Wong,
H.Meier-Ewert,
J.J.Skehel,
and
D.C.Wiley
(1999).
X-ray crystallographic determination of the structure of the influenza C virus haemagglutinin-esterase-fusion glycoprotein.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
945-961.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Weissenhorn,
A.Carfí,
K.H.Lee,
J.J.Skehel,
and
D.C.Wiley
(1998).
Crystal structure of the Ebola virus membrane fusion subunit, GP2, from the envelope glycoprotein ectodomain.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
2,
605-616.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

