 |
PDBsum entry 1cg0

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.4
- adenylosuccinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP and GMP Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
IMP + L-aspartate + GTP = N6-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP + GDP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
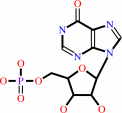 IMP
IMP
|
+
|
L-aspartate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.19% similarity
|
+
|
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
=
|
N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
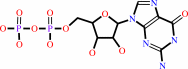 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
38:6953-6961
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanistic implications from crystalline complexes of wild-type and mutant adenylosuccinate synthetases from Escherichia coli.
|
|
J.Y.Choe,
B.W.Poland,
H.J.Fromm,
R.B.Honzatko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Asp13 and His41 are essential residues of adenylosuccinate synthetase,
putatively catalyzing the formation of adenylosuccinate from an intermediate of
6-phosphoryl-IMP. Wild-type adenylosuccinate synthetase and three mutant
synthetases (Arg143 --> Leu, Lys16 --> Gln, and Arg303 --> Leu) from
Eschericha coli have been crystallized in the presence of IMP, hadacidin (an
analogue of L-aspartate), Mg2+, and GTP. The active site of each complex
contains 6-phosphoryl-IMP, Mg2+, GDP, and hadacidin, except for the Arg303
--> Leu mutant, which does not bind hadacidin. In response to the formation
of 6-phosphoryl-IMP, Asp13 enters the inner coordination sphere of the active
site Mg2+. His41 hydrogen bonds with 6-phosphoryl-IMP, except in the Arg303
--> Leu complex, where it remains bound to the guanine nucleotide. Hence,
recognition of the active site Mg2+ by Asp13 evidently occurs after the
formation of 6-phosphoryl-IMP, but recognition of the intermediate by His41 may
require the association of L-aspartate with the active site. Structures reported
here support a mechanism in which Asp13 and His41 act as the catalytic base and
acid, respectively, in the formation of 6-phosphoryl-IMP, and then act together
as catalytic acids in the subsequent formation of adenylosuccinate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.D.Ginder,
D.J.Binkowski,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2006).
Nucleotide complexes of Escherichia coli phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
20680-20688.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Sun,
N.Li,
X.Wang,
T.Chen,
L.Shi,
L.Zhang,
J.Wang,
T.Wan,
and
X.Cao
(2005).
Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel muscle adenylosuccinate synthetase, AdSSL1, from human bone marrow stromal cells.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biochem,
269,
85-94.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Borza,
C.V.Iancu,
E.Pike,
R.B.Honzatko,
and
H.J.Fromm
(2003).
Variations in the response of mouse isozymes of adenylosuccinate synthetase to inhibitors of physiological relevance.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
6673-6679.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Gorrell,
W.Wang,
E.Underbakke,
Z.Hou,
R.B.Honzatko,
and
H.J.Fromm
(2002).
Determinants of L-aspartate and IMP recognition in Escherichia coli adenylosuccinate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
8817-8821.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.V.Iancu,
T.Borza,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2002).
IMP, GTP, and 6-phosphoryl-IMP complexes of recombinant mouse muscle adenylosuccinate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
26779-26787.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.V.Iancu,
T.Borza,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2002).
Feedback inhibition and product complexes of recombinant mouse muscle adenylosuccinate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
40536-40543.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.V.Iancu,
T.Borza,
J.Y.Choe,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2001).
Recombinant mouse muscle adenylosuccinate synthetase: overexpression, kinetics, and crystal structure.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
42146-42152.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

