 |
PDBsum entry 1ca7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.2.1
- phenylpyruvate tautomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phenylpyruvate = enol-phenylpyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phenylpyruvate
|
=
|
enol-phenylpyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 92.31% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.12
- L-dopachrome isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dopachrome = 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-dopachrome
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 80.00% similarity
|
=
|
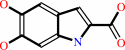 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
38:7346-7354
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Pro-1 of macrophage migration inhibitory factor functions as a catalytic base in the phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity.
|
|
J.B.Lubetsky,
M.Swope,
C.Dealwis,
P.Blake,
E.Lolis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is an important immunoregulatory
molecule with a unique ability to suppress the anti-inflammatory effects of
glucocorticoids. Although considered a cytokine, MIF possesses a
three-dimensional structure and active site similar to those of 4-oxalocrotonate
tautomerase and 5-carboxymethyl-2-hydroxymuconate isomerase. Moreover, a number
of catalytic activities have been defined for MIF. To gain insight into the role
of catalysis in the biological function of MIF, we have begun to characterize
the catalytic activities in more detail. Here we report the crystal structure of
MIF complexed with p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate, a substrate for the phenylpyruvate
tautomerase activity of MIF. The three binding sites for p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate
in the MIF trimer lie at the interface between two subunits. The substrate
interacts with Pro-1, Lys-32, and Ile-64 from one subunit and Tyr-95 and Asn-97
from an adjacent subunit. Pro-1 is positioned to function as a catalytic base.
There is no functional group that polarizes the alpha-carbonyl of the substrate
to weaken the adjacent C-H bond. Mutation of Pro-1 to glycine substantially
reduces the catalytic activity. The insertion of an alanine between Pro-1 and
Met-2 essentially abolishes activity. Structural studies of these mutants define
a source of the reduced activity and provide insight into the mechanism of the
catalytic reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Kimura,
Y.Sato,
Y.Tajima,
H.Suzuki,
H.Yukitake,
T.Imaeda,
M.Kajino,
H.Oki,
M.Takizawa,
and
S.Tanida
(2010).
BTZO-1, a cardioprotective agent, reveals that macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulates ARE-mediated gene expression.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
1282-1294.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.E.Rendon,
S.S.Willer,
W.Zundel,
and
R.A.Mitchell
(2009).
Mechanisms of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-dependent tumor microenvironmental adaptation.
|
| |
Exp Mol Pathol,
86,
180-185.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow,
J.B.Lubetsky,
L.Leng,
R.Bucala,
and
E.J.Lolis
(2009).
Structural and kinetic analyses of macrophage migration inhibitory factor active site interactions.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
132-139.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Dobson,
K.D.Augustijn,
J.A.Brannigan,
C.Schnick,
C.J.Janse,
E.J.Dodson,
A.P.Waters,
and
A.J.Wilkinson
(2009).
The crystal structures of macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium berghei.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
2578-2591.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Cournia,
L.Leng,
S.Gandavadi,
X.Du,
R.Bucala,
and
W.L.Jorgensen
(2009).
Discovery of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-CD74 antagonists via virtual screening.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
416-424.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Kamir,
S.Zierow,
L.Leng,
Y.Cho,
Y.Diaz,
J.Griffith,
C.McDonald,
M.Merk,
R.A.Mitchell,
J.Trent,
Y.Chen,
Y.K.Kwong,
H.Xiong,
J.Vermeire,
M.Cappello,
D.McMahon-Pratt,
J.Walker,
J.Bernhagen,
E.Lolis,
and
R.Bucala
(2008).
A Leishmania ortholog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates host macrophage responses.
|
| |
J Immunol,
180,
8250-8261.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Poelarends,
V.P.Veetil,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2008).
The chemical versatility of the beta-alpha-beta fold: catalytic promiscuity and divergent evolution in the tautomerase superfamily.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
3606-3618.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.R.Parrish,
M.Gallowitsch-Puerta,
C.J.Czura,
and
K.J.Tracey
(2008).
Experimental therapeutic strategies for severe sepsis: mediators and mechanisms.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1144,
210-236.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Poelarends,
W.H.Johnson,
H.Serrano,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2007).
Phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity of trans-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase: evidence for an enol intermediate in the dehalogenase reaction?
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
9596-9604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow,
K.F.Cheng,
D.Dabideen,
M.Ochani,
B.Aljabari,
V.A.Pavlov,
E.J.Miller,
E.Lolis,
and
Y.Al-Abed
(2007).
Alternative chemical modifications reverse the binding orientation of a pharmacophore scaffold in the active site of macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
23089-23095.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Augustijn,
R.Kleemann,
J.Thompson,
T.Kooistra,
C.E.Crawford,
S.E.Reece,
A.Pain,
A.H.Siebum,
C.J.Janse,
and
A.P.Waters
(2007).
Functional characterization of the Plasmodium falciparum and P. berghei homologues of macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
75,
1116-1128.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Wang,
W.H.Johnson,
R.M.Czerwinski,
S.L.Stamps,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2007).
Kinetic and stereochemical analysis of YwhB, a 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase homologue in Bacillus subtilis: mechanistic implications for the YwhB- and 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase-catalyzed reactions.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
11919-11929.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cho,
B.F.Jones,
J.J.Vermeire,
L.Leng,
L.DiFedele,
L.M.Harrison,
H.Xiong,
Y.K.Kwong,
Y.Chen,
R.Bucala,
E.Lolis,
and
M.Cappello
(2007).
Structural and functional characterization of a secreted hookworm Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) that interacts with the human MIF receptor CD74.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
23447-23456.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.F.Morand,
M.Leech,
and
J.Bernhagen
(2006).
MIF: a new cytokine link between rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
5,
399-410.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Wilson,
P.L.Coletta,
R.J.Cuthbert,
N.Scott,
K.MacLennan,
G.Hawcroft,
L.Leng,
J.B.Lubetsky,
K.K.Jin,
E.Lolis,
F.Medina,
J.A.Brieva,
R.Poulsom,
A.F.Markham,
R.Bucala,
and
M.A.Hull
(2005).
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes intestinal tumorigenesis.
|
| |
Gastroenterology,
129,
1485-1503.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Thiele,
and
J.Bernhagen
(2005).
Link between macrophage migration inhibitory factor and cellular redox regulation.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
7,
1234-1248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Al-Abed,
D.Dabideen,
B.Aljabari,
A.Valster,
D.Messmer,
M.Ochani,
M.Tanovic,
K.Ochani,
M.Bacher,
F.Nicoletti,
C.Metz,
V.A.Pavlov,
E.J.Miller,
and
K.J.Tracey
(2005).
ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
36541-36544.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Joseph-McCarthy,
B.E.Thomas,
M.Belmarsh,
D.Moustakas,
and
J.C.Alvarez
(2003).
Pharmacophore-based molecular docking to account for ligand flexibility.
|
| |
Proteins,
51,
172-188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Joseph-McCarthy,
and
J.C.Alvarez
(2003).
Automated generation of MCSS-derived pharmacophoric DOCK site points for searching multiconformation databases.
|
| |
Proteins,
51,
189-202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Lolis,
and
R.Bucala
(2003).
Therapeutic approaches to innate immunity: severe sepsis and septic shock.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
635-645.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Lolis,
and
R.Bucala
(2003).
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
7,
153-164.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Potolicchio,
L.Santambrogio,
and
J.L.Strominger
(2003).
Molecular interaction and enzymatic activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor with immunorelevant peptides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
30889-30895.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Nguyen,
J.Beck,
H.Lue,
H.Fünfzig,
R.Kleemann,
P.Koolwijk,
A.Kapurniotu,
and
J.Bernhagen
(2003).
A 16-residue peptide fragment of macrophage migration inhibitory factor, MIF-(50-65), exhibits redox activity and has MIF-like biological functions.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
33654-33671.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Baugh,
and
R.Bucala
(2002).
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
|
| |
Crit Care Med,
30,
S27-S35.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Lubetsky,
A.Dios,
J.Han,
B.Aljabari,
B.Ruzsicska,
R.Mitchell,
E.Lolis,
and
Y.Al-Abed
(2002).
The tautomerase active site of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential target for discovery of novel anti-inflammatory agents.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
24976-24982.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Senter,
Y.Al-Abed,
C.N.Metz,
F.Benigni,
R.A.Mitchell,
J.Chesney,
J.Han,
C.G.Gartner,
S.D.Nelson,
G.J.Todaro,
and
R.Bucala
(2002).
Inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) tautomerase and biological activities by acetaminophen metabolites.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
144-149.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Soares,
R.D.Lins,
T.P.Straatsma,
and
J.M.Briggs
(2002).
Internal dynamics and ionization states of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor: comparison between wild-type and mutant forms.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
65,
313-323.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zang,
P.Taylor,
J.M.Wang,
D.J.Meyer,
A.L.Scott,
M.D.Walkinshaw,
and
R.M.Maizels
(2002).
Homologues of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor from a parasitic nematode. Gene cloning, protein activity, and crystal structure.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
44261-44267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Poelarends,
R.Saunier,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2001).
trans-3-Chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas pavonaceae 170 shares structural and mechanistic similarities with 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
4269-4277.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Kleemann,
H.Rorsman,
E.Rosengren,
R.Mischke,
N.T.Mai,
and
J.Bernhagen
(2000).
Dissection of the enzymatic and immunologic functions of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Full immunologic activity of N-terminally truncated mutants.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
267,
7183-7193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Stamps,
A.B.Taylor,
S.C.Wang,
M.L.Hackert,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2000).
Mechanism of the phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor: properties of the P1G, P1A, Y95F, and N97A mutants.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
9671-9678.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Soares,
D.Goodsell,
R.Ferreira,
A.J.Olson,
and
J.M.Briggs
(2000).
Ionization state and molecular docking studies for the macrophage migration inhibitory factor: the role of lysine 32 in the catalytic mechanism.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
13,
146-156.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

