 |
PDBsum entry 1b8f

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.3
- histidine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Histidine Catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-histidine = trans-urocanate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
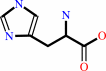 L-histidine
L-histidine
|
=
|
trans-urocanate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
38:5355-5361
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of histidine ammonia-lyase revealing a novel polypeptide modification as the catalytic electrophile.
|
|
T.F.Schwede,
J.Rétey,
G.E.Schulz.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Histidine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.3) catalyzes the nonoxidative elimination of
the alpha-amino group of histidine and is closely related to the important plant
enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. The crystal structure of histidase from
Pseudomonas putida was determined at 2.1 A resolution revealing a homotetramer
with D2 symmetry, the molecular center of which is formed by 20 nearly parallel
alpha-helices. The chain fold, but not the sequence, resembles those of fumarase
C and related proteins. The structure shows that the reactive electrophile is a
4-methylidene-imidazole-5-one, which is formed autocatalytically by cyclization
and dehydration of residues 142-144 with the sequence Ala-Ser-Gly. With respect
to the first dehydration step, this modification resembles the chromophore of
the green fluorescent protein. The active center is clearly established by the
modification and by mutations. The observed geometry allowed us to model the
bound substrate at a high confidence level. A reaction mechanism is proposed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.J.Turner
(2011).
Ammonia lyases and aminomutases as biocatalysts for the synthesis of α-amino and β-amino acids.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
15,
234-240.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Wang
(2011).
Structure, function, and engineering of enzymes in isoflavonoid biosynthesis.
|
| |
Funct Integr Genomics,
11,
13-22.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Cooke,
and
S.D.Bruner
(2010).
Probing the active site of MIO-dependent aminomutases, key catalysts in the biosynthesis of beta-amino acids incorporated in secondary metabolites.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
93,
802-810.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Hayashi,
S.Tanase,
and
T.Yagi
(2010).
Esmond E. Snell--the pathfinder of B vitamins and cofactors.
|
| |
J Biochem,
147,
451-457.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bartsch,
and
U.T.Bornscheuer
(2010).
Mutational analysis of phenylalanine ammonia lyase to improve reactions rates for various substrates.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
929-933.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Pakhomov,
and
V.I.Martynov
(2009).
Posttranslational chemistry of proteins of the GFP family.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
74,
250-259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Wu,
W.Szymanski,
P.Wietzes,
S.de Wildeman,
G.J.Poelarends,
B.L.Feringa,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2009).
Enzymatic Synthesis of Enantiopure alpha- and beta-Amino Acids by Phenylalanine Aminomutase-Catalysed Amination of Cinnamic Acid Derivatives.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
338-344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Cooke,
C.V.Christianson,
and
S.D.Bruner
(2009).
Structure and chemistry of 4-methylideneimidazole-5-one containing enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
460-468.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Mishin,
F.V.Subach,
I.V.Yampolsky,
W.King,
K.A.Lukyanov,
and
V.V.Verkhusha
(2008).
The first mutant of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein that forms a red chromophore.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
4666-4673.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Davin,
M.Jourdes,
A.M.Patten,
K.W.Kim,
D.G.Vassão,
and
N.G.Lewis
(2008).
Dissection of lignin macromolecular configuration and assembly: Comparison to related biochemical processes in allyl/propenyl phenol and lignan biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
25,
1015-1090.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.P.Lemay,
A.L.Morgan,
E.J.Archer,
L.A.Dickson,
C.M.Megley,
and
M.Zimmer
(2008).
The Role of the Tight-Turn, Broken Hydrogen Bonding, Glu222 and Arg96 in the Post-translational Green Fluorescent Protein Chromophore Formation.
|
| |
Chem Phys,
348,
152-160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.S.Sariaslani
(2007).
Development of a combined biological and chemical process for production of industrial aromatics from renewable resources.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
61,
51-69.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Mocz
(2007).
Fluorescent proteins and their use in marine biosciences, biotechnology, and proteomics.
|
| |
Mar Biotechnol (NY),
9,
305-328.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Moffitt,
G.V.Louie,
M.E.Bowman,
J.Pence,
J.P.Noel,
and
B.S.Moore
(2007).
Discovery of two cyanobacterial phenylalanine ammonia lyases: kinetic and structural characterization.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
1004-1012.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.MacDonald,
and
G.B.D'Cunha
(2007).
A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase.
|
| |
Biochem Cell Biol,
85,
273-282.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.X.Zhang,
and
P.B.Rainey
(2007).
Genetic analysis of the histidine utilization (hut) genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25.
|
| |
Genetics,
176,
2165-2176.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Xue,
M.McCluskey,
K.Cantera,
F.S.Sariaslani,
and
L.Huang
(2007).
Identification, characterization and functional expression of a tyrosine ammonia-lyase and its mutants from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides.
|
| |
J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol,
34,
599-604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Katona,
M.I.Toşa,
C.Paizs,
and
J.Rétey
(2006).
Inhibition of histidine ammonia lyase by heteroaryl-alanines and acrylates.
|
| |
Chem Biodivers,
3,
502-508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.V.Louie,
M.E.Bowman,
M.C.Moffitt,
T.J.Baiga,
B.S.Moore,
and
J.P.Noel
(2006).
Structural determinants and modulation of substrate specificity in phenylalanine-tyrosine ammonia-lyases.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
13,
1327-1338.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.T.Watts,
B.N.Mijts,
P.C.Lee,
A.J.Manning,
and
C.Schmidt-Dannert
(2006).
Discovery of a substrate selectivity switch in tyrosine ammonia-lyase, a member of the aromatic amino acid lyase family.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
13,
1317-1326.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Berner,
D.Krug,
C.Bihlmaier,
A.Vente,
R.Müller,
and
A.Bechthold
(2006).
Genes and enzymes involved in caffeic acid biosynthesis in the actinomycete Saccharothrix espanaensis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
2666-2673.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Remington
(2006).
Fluorescent proteins: maturation, photochemistry and photophysics.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
16,
714-721.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pilbák,
A.Tomin,
J.Rétey,
and
L.Poppe
(2006).
The essential tyrosine-containing loop conformation and the role of the C-terminal multi-helix region in eukaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyases.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
1004-1019.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yu,
Y.H.Liang,
E.Brostromer,
J.M.Quan,
S.Panjikar,
Y.H.Dong,
and
X.D.Su
(2006).
A catalytic mechanism revealed by the crystal structures of the imidazolonepropionase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
36929-36936.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Walsh,
S.Garneau-Tsodikova,
and
G.J.Gatto
(2005).
Protein posttranslational modifications: the chemistry of proteome diversifications.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
7342-7372.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Poppe,
and
J.Rétey
(2005).
Friedel-Crafts-type mechanism for the enzymatic elimination of ammonia from histidine and phenylalanine.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
3668-3688.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Buckel,
B.M.Martins,
A.Messerschmidt,
and
B.T.Golding
(2005).
Radical-mediated dehydration reactions in anaerobic bacteria.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
386,
951-959.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Asano,
I.Kira,
and
K.Yokozeki
(2005).
Alteration of substrate specificity of aspartase by directed evolution.
|
| |
Biomol Eng,
22,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Walker,
K.Klettke,
T.Akiyama,
and
R.Croteau
(2004).
Cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of a phenylalanine aminomutase involved in Taxol biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
53947-53954.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Barondeau,
C.D.Putnam,
C.J.Kassmann,
J.A.Tainer,
and
E.D.Getzoff
(2003).
Mechanism and energetics of green fluorescent protein chromophore synthesis revealed by trapped intermediate structures.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
12111-12116.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Christenson,
W.Wu,
M.A.Spies,
B.Shen,
and
M.D.Toney
(2003).
Kinetic analysis of the 4-methylideneimidazole-5-one-containing tyrosine aminomutase in enediyne antitumor antibiotic C-1027 biosynthesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
12708-12718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Levy,
P.A.Buckley,
S.Sedelnikova,
Y.Kato,
Y.Asano,
D.W.Rice,
and
P.J.Baker
(2002).
Insights into enzyme evolution revealed by the structure of methylaspartate ammonia lyase.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
105-113.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Röther,
L.Poppe,
G.Morlock,
S.Viergutz,
and
J.Rétey
(2002).
An active site homology model of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Petroselinum crispum.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
3065-3075.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Xiang,
and
B.S.Moore
(2002).
Inactivation, complementation, and heterologous expression of encP, a novel bacterial phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
32505-32509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Asuncion,
W.Blankenfeldt,
J.N.Barlow,
D.Gani,
and
J.H.Naismith
(2002).
The structure of 3-methylaspartase from Clostridium tetanomorphum functions via the common enolase chemical step.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
8306-8311.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Baedeker,
and
G.E.Schulz
(2002).
Structures of two histidine ammonia-lyase modifications and implications for the catalytic mechanism.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
1790-1797.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Matz,
K.A.Lukyanov,
and
S.A.Lukyanov
(2002).
Family of the green fluorescent protein: journey to the end of the rainbow.
|
| |
Bioessays,
24,
953-959.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Levy,
P.A.Buckley,
P.J.Baker,
S.Sedelnikova,
F.Rodgers,
Y.F.Li,
Y.Kato,
Y.Asano,
and
D.W.Rice
(2001).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of Citrobacter amalonaticus methylaspartate ammonia lyase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
1922-1924.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Röther,
L.Poppe,
S.Viergutz,
B.Langer,
and
J.Rétey
(2001).
Characterization of the active site of histidine ammonia-lyase from Pseudomonas putida.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
6011-6019.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Poppe
(2001).
Methylidene-imidazolone: a novel electrophile for substrate activation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
5,
512-524.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Xie,
and
W.A.van der Donk
(2001).
Homemade cofactors: self-processing in galactose oxidase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
12863-12865.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Asuncion,
J.N.Barlow,
J.Pollard,
A.G.Staines,
S.A.McMahon,
W.Blankenfeldt,
D.Gani,
and
J.H.Naismith
(2001).
Overexpression, purification, crystallization and data collection of 3-methylaspartase from Clostridium tetanomorphum.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
731-733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Piel,
C.Hertweck,
P.R.Shipley,
D.M.Hunt,
M.S.Newman,
and
B.S.Moore
(2000).
Cloning, sequencing and analysis of the enterocin biosynthesis gene cluster from the marine isolate 'Streptomyces maritimus': evidence for the derailment of an aromatic polyketide synthase.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
7,
943-955.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.M.Okeley,
and
W.A.van der Donk
(2000).
Novel cofactors via post-translational modifications of enzyme active sites.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
7,
R159-R171.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Dickert,
A.J.Pierik,
D.Linder,
and
W.Buckel
(2000).
The involvement of coenzyme A esters in the dehydration of (R)-phenyllactate to (E)-cinnamate by Clostridium sporogenes.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
267,
3874-3884.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

