 |
PDBsum entry 1a8h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1a8h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Methionyl-tRNA synthetase from thermus thermophilus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Chain: a. Synonym: metrs. Other_details: zn in zn finger
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus. Organism_taxid: 300852. Strain: hb8
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.205
|
R-free:
|
0.283
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
I.Sugiura,O.Nureki,Y.Ugaji,S.Kuwabara,B.Lober,R.Giege,D.Moras, S.Yokoyama,M.Konno,Riken Structural Genomics/proteomics Initiative (Rsgi)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
I.Sugiura
et al.
(2000).
The 2.0 A crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus methionyl-tRNA synthetase reveals two RNA-binding modules.
Structure,
8,
197-208.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
26-Mar-98
|
Release date:
|
04-May-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P23395
(SYM_THET8) -
Methionine--tRNA ligase from Thermus thermophilus (strain ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / HB8)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
618 a.a.
500 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.10
- methionine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Met) + L-methionine + ATP = L-methionyl-tRNA(Met) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
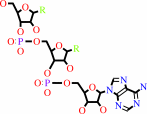 tRNA(Met)
tRNA(Met)
|
+
|
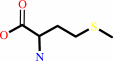 L-methionine
L-methionine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
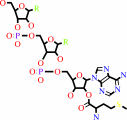 L-methionyl-tRNA(Met)
L-methionyl-tRNA(Met)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Structure
8:197-208
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The 2.0 A crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus methionyl-tRNA synthetase reveals two RNA-binding modules.
|
|
I.Sugiura,
O.Nureki,
Y.Ugaji-Yoshikawa,
S.Kuwabara,
A.Shimada,
M.Tateno,
B.Lorber,
R.Giegé,
D.Moras,
S.Yokoyama,
M.Konno.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: The 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are divided into two classes, I
and II. The 10 class I synthetases are considered to have in common the
catalytic domain structure based on the Rossmann fold, which is totally
different from the class II catalytic domain structure. The class I synthetases
are further divided into three subclasses, a, b and c, according to sequence
homology. No conserved structural features for tRNA recognition by class I
synthetases have been established. RESULTS: We determined the crystal structure
of the class Ia methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MetRS) at 2.0 A resolution, using
MetRS from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus HB8. The T. thermophilus
MetRS structure is in full agreement with the biochemical and genetic data from
Escherichia coli MetRS. The conserved 'anticodon-binding' residues are spatially
clustered on an alpha-helix-bundle domain. The Rossmann-fold and
anticodon-binding domains are connected by a beta-alpha-alpha-beta-alpha
topology ('SC fold') domain that contains the class I specific KMSKS motif.
CONCLUSIONS: The alpha-helix-bundle domain identified in the MetRS structure is
the signature of the class Ia enzymes, as it was also identified in the class Ia
structures of the isoleucyl- and arginyl-tRNA synthetases. The
beta-alpha-alpha-beta-alpha topology domain, which can now be identified in all
known structures of the class Ia and Ib synthetases, is likely to dock with the
inner side of the L-shaped tRNA, thereby positioning the anticodon stem.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Ingvarsson,
and
T.Unge
(2010).
Flexibility and communication within the structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis methionyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
3947-3962.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Fan,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2009).
Toward the catalytic mechanism of a cysteine ligase (MshC) from Mycobacterium smegmatis: an enzyme involved in the biosynthetic pathway of mycothiol.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
7150-7159.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Velázquez-Muriel,
M.Rueda,
I.Cuesta,
A.Pascual-Montano,
M.Orozco,
and
J.M.Carazo
(2009).
Comparison of molecular dynamics and superfamily spaces of protein domain deformation.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Nakanishi,
L.Bonnefond,
S.Kimura,
T.Suzuki,
R.Ishitani,
and
O.Nureki
(2009).
Structural basis for translational fidelity ensured by transfer RNA lysidine synthetase.
|
| |
Nature,
461,
1144-1148.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.T.Doan,
S.Natarajan,
H.Kim,
Y.J.Ahn,
J.G.Kim,
B.M.Lee,
and
L.W.Kang
(2009).
Cloning, expression, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (Xoo1504) from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
51-54.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Rorbach,
A.A.Yusoff,
H.Tuppen,
D.P.Abg-Kamaludin,
Z.M.Chrzanowska-Lightowlers,
R.W.Taylor,
D.M.Turnbull,
R.McFarland,
and
R.N.Lightowlers
(2008).
Overexpression of human mitochondrial valyl tRNA synthetase can partially restore levels of cognate mt-tRNAVal carrying the pathogenic C25U mutation.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
3065-3074.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Tremblay,
F.Fan,
M.W.Vetting,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2008).
The 1.6 A crystal structure of Mycobacterium smegmatis MshC: the penultimate enzyme in the mycothiol biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
13326-13335.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Budiman,
M.H.Knaggs,
J.S.Fetrow,
and
R.W.Alexander
(2007).
Using molecular dynamics to map interaction networks in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Proteins,
68,
670-689.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.I.Jones,
A.C.Spencer,
J.L.Hsu,
L.L.Spremulli,
S.A.Martinis,
M.DeRider,
and
P.F.Agris
(2006).
A counterintuitive Mg2+-dependent and modification-assisted functional folding of mitochondrial tRNAs.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
362,
771-786.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Han,
N.Kerrison,
C.Chothia,
and
S.A.Teichmann
(2006).
Divergence of interdomain geometry in two-domain proteins.
|
| |
Structure,
14,
935-945.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Roach,
S.Sharma,
M.Kapustina,
and
C.W.Carter
(2005).
Structure alignment via Delaunay tetrahedralization.
|
| |
Proteins,
60,
66-81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Nakanishi,
Y.Ogiso,
T.Nakama,
S.Fukai,
and
O.Nureki
(2005).
Structural basis for anticodon recognition by methionyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
12,
931-932.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sakurai,
T.Ohtsuki,
and
K.Watanabe
(2005).
Modification at position 9 with 1-methyladenosine is crucial for structure and function of nematode mitochondrial tRNAs lacking the entire T-arm.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
33,
1653-1661.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hauenstein,
C.M.Zhang,
Y.M.Hou,
and
J.J.Perona
(2004).
Shape-selective RNA recognition by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
1134-1141.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.G.Zheng,
H.Wei,
C.Ling,
F.Martin,
G.Eriani,
and
E.D.Wang
(2004).
Two distinct domains of the beta subunit of Aquifex aeolicus leucyl-tRNA synthetase are involved in tRNA binding as revealed by a three-hybrid selection.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
32,
3294-3303.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Ferré-D'Amaré
(2003).
RNA-modifying enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
13,
49-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.S.Laursen,
K.K.Mortensen,
H.U.Sperling-Petersen,
and
D.W.Hoffman
(2003).
A conserved structural motif at the N terminus of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
16320-16328.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.D.Sherlin,
and
J.J.Perona
(2003).
tRNA-dependent active site assembly in a class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
591-603.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fukai,
O.Nureki,
S.Sekine,
A.Shimada,
D.G.Vassylyev,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2003).
Mechanism of molecular interactions for tRNA(Val) recognition by valyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
RNA,
9,
100-111.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Newberry,
Y.M.Hou,
and
J.J.Perona
(2002).
Structural origins of amino acid selection without editing by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
2778-2787.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kitabatake,
K.Ali,
A.Demain,
K.Sakamoto,
S.Yokoyama,
and
D.Söll
(2002).
Indolmycin resistance of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) by induced expression of one of its two tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
23882-23887.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Terada,
O.Nureki,
R.Ishitani,
A.Ambrogelly,
M.Ibba,
D.Söll,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2002).
Functional convergence of two lysyl-tRNA synthetases with unrelated topologies.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
257-262.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Shimada,
O.Nureki,
M.Goto,
S.Takahashi,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2001).
Structural and mutational studies of the recognition of the arginine tRNA-specific major identity element, A20, by arginyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
13537-13542.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Nureki,
S.Fukai,
S.Sekine,
A.Shimada,
T.Terada,
T.Nakama,
M.Shirouzu,
D.G.Vassylyev,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2001).
Structural basis for amino acid and tRNA recognition by class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol,
66,
167-173.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kaminska,
M.Deniziak,
P.Kerjan,
J.Barciszewski,
and
M.Mirande
(2000).
A recurrent general RNA binding domain appended to plant methionyl-tRNA synthetase acts as a cis-acting cofactor for aminoacylation.
|
| |
EMBO J,
19,
6908-6917.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Cusack,
A.Yaremchuk,
and
M.Tukalo
(2000).
The 2 A crystal structure of leucyl-tRNA synthetase and its complex with a leucyl-adenylate analogue.
|
| |
EMBO J,
19,
2351-2361.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

